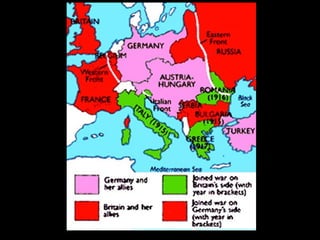
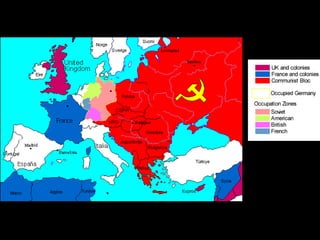
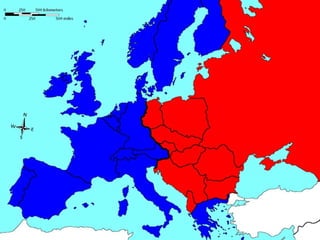
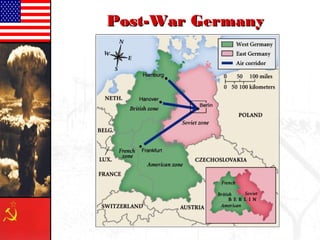
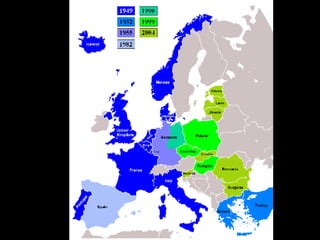
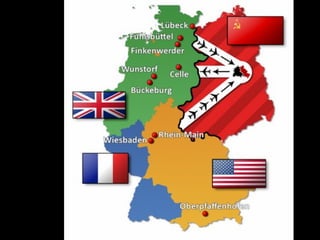
The document provides information about the origins and impact of the Cold War. It discusses how after WWII, tensions grew between the Western allies (US, UK, France) and the Soviet Union over the political and economic systems in Eastern Europe. This led to the division of Europe and Germany into capitalist and communist spheres of influence separated by the Iron Curtain. Over time, the US and USSR built up opposing military alliances (NATO and Warsaw Pact) and stockpiles of nuclear weapons in a tense standoff known as the Cold War, which impacted global politics until the Soviet Union's collapse in 1991.