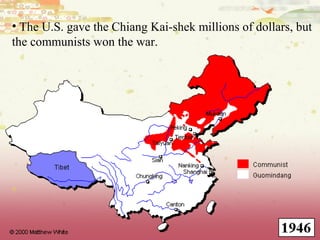
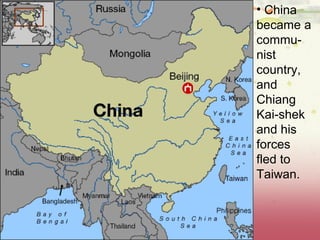
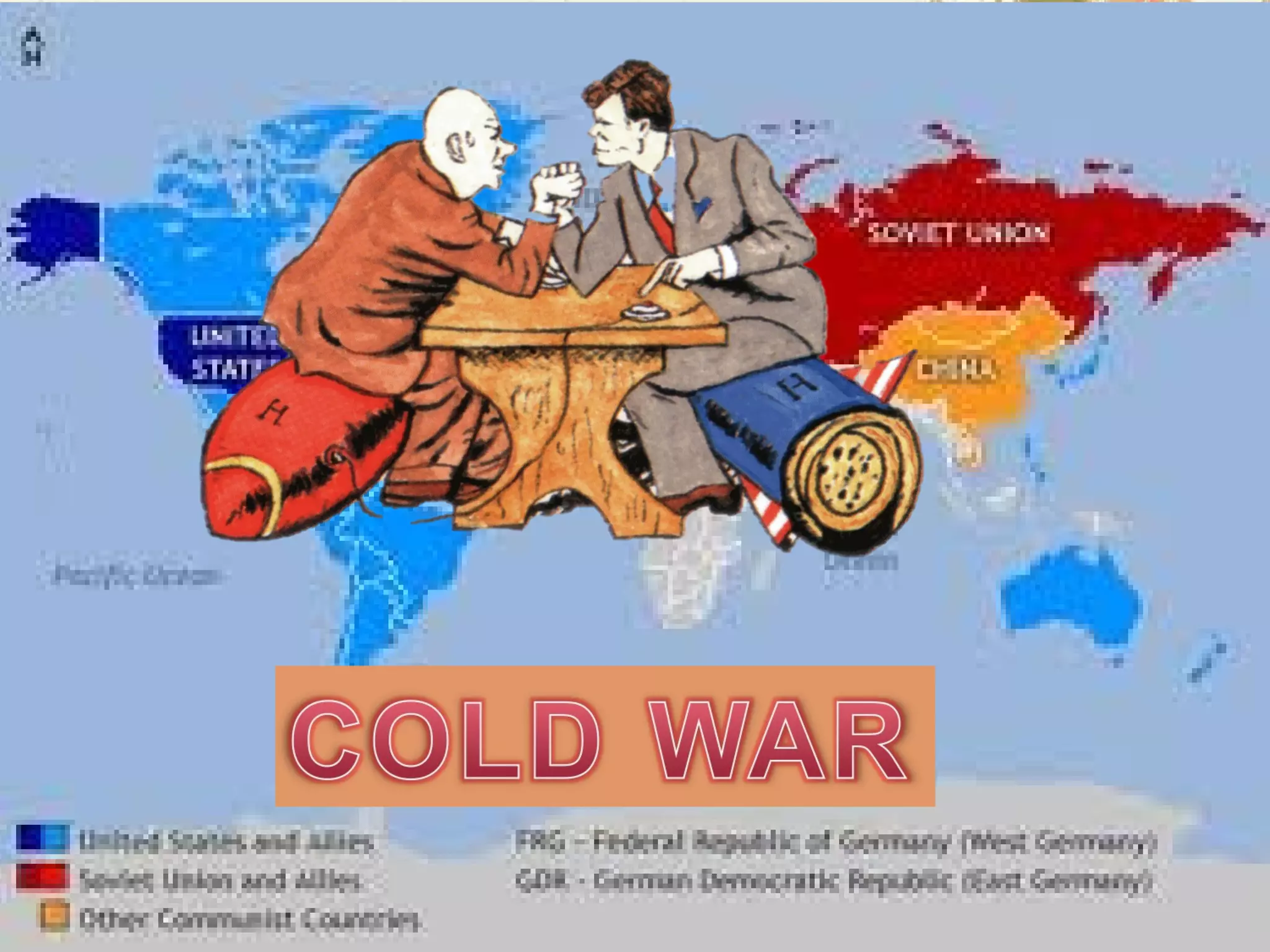
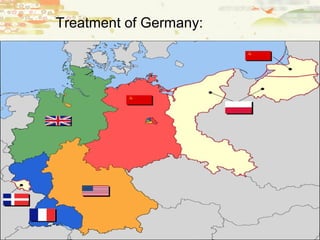
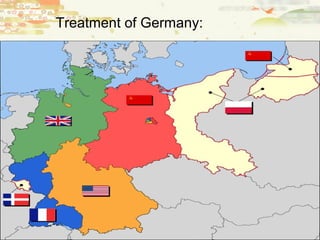
Germany surrendered in 1945 and was divided and occupied by the Allies. The Potsdam Conference established this division and began de-Nazification efforts. Europe was largely bankrupt after the war while the US and USSR emerged as new superpowers. The Soviets wanted to rebuild the German economy to their benefit while the Americans prioritized self-determination, leading to the origins of the Cold War between them. Japan also surrendered in 1945 after atomic bombs were dropped and was remade under US occupation with a new constitution and demilitarization. These postwar changes established the foundations for the ensuing global Cold War conflict between capitalist and communist ideologies.
















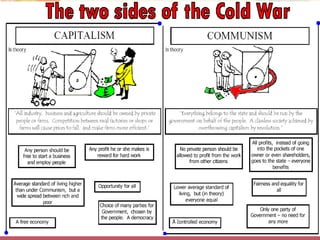


![The Ideological Struggle
Soviet & US & the
Eastern Bloc Western
Nations Democracies
[“Iron Curtain”]
GOAL
GOAL spread world-wide “Containment” of
Communism Communism & the
eventual collapse of
METHODOLOGIES:
the Communist world.
Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] [George Kennan]
Arms Race [nuclear escalation]
Ideological Competition for the minds and hearts
of Third World peoples [Communist govt. &
command economy vs. democratic govt. & capitalist
economy] “proxy wars”
Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecoldwar-130217195108-phpapp01/85/The-Cold-War-24-320.jpg)











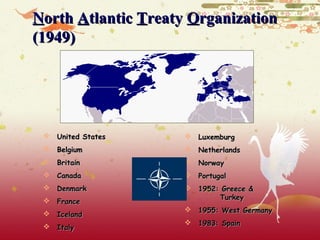
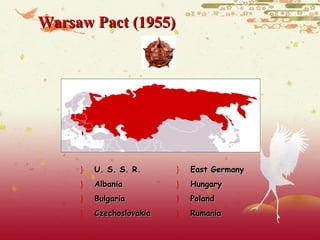


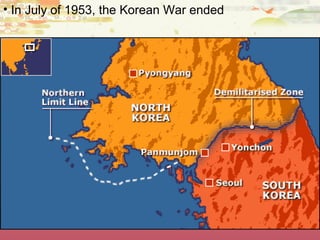
![Korean War
[1950-1953]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecoldwar-130217195108-phpapp01/85/The-Cold-War-43-320.jpg)
![Korean War
[1950-1953]
Kim Il-Sung
Syngman Rhee
“Domino Theory”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecoldwar-130217195108-phpapp01/85/The-Cold-War-44-320.jpg)


![The Shifting Map of Korea
[1950-1953]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecoldwar-130217195108-phpapp01/85/The-Cold-War-47-320.jpg)