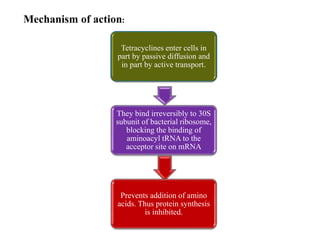
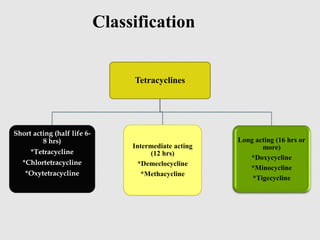
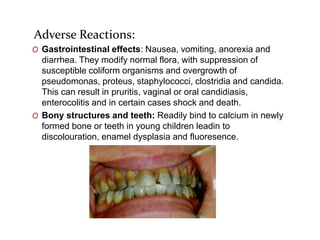
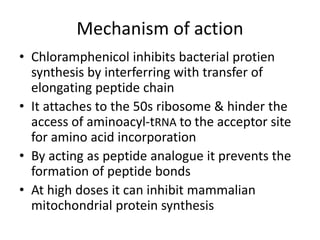
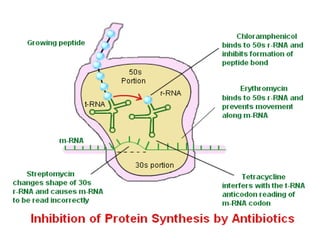
Tetracyclines are broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by binding irreversibly to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. They are classified based on duration of action into short, intermediate, and long-acting drugs. Tetracyclines are absorbed orally but absorption is impaired by food and antacids. They are used to treat infections caused by mycoplasma, chlamydia, rickettsiae, and certain bacterial and atypical mycobacterial infections. Adverse effects include gastrointestinal issues and photosensitivity.