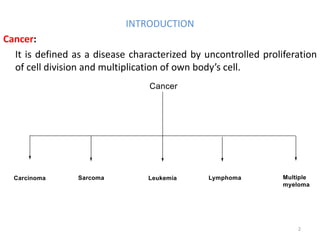
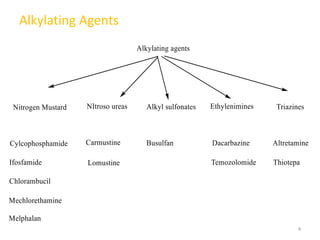
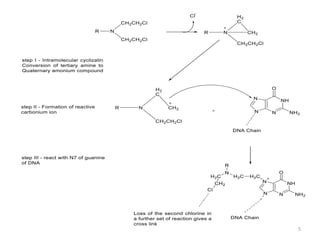
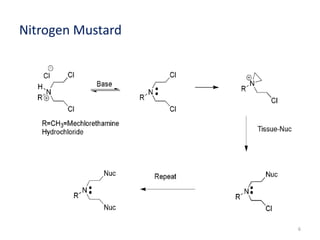
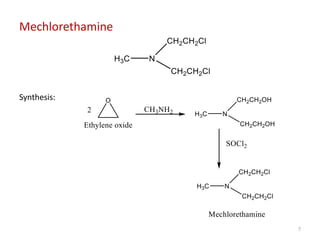
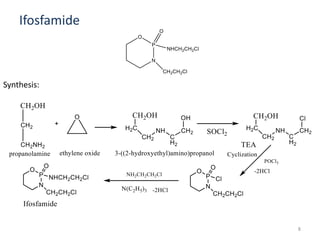
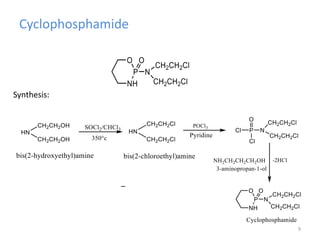
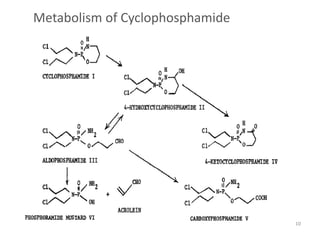
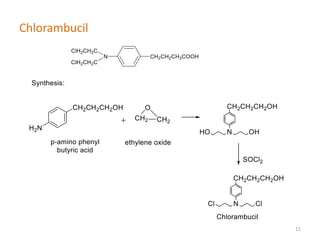
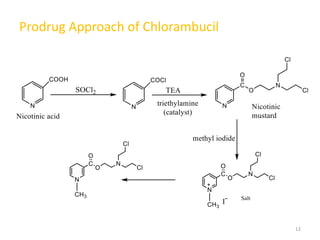
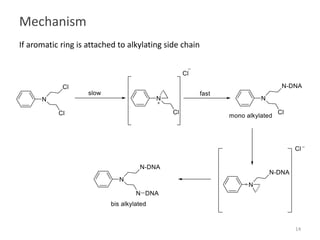
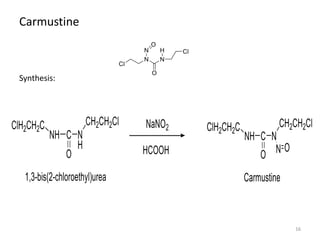
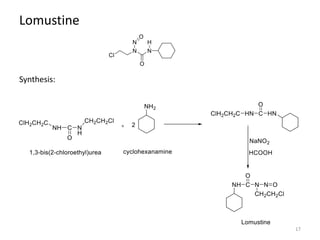
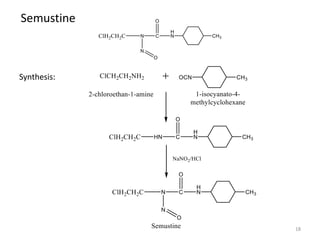
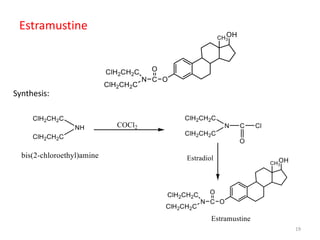
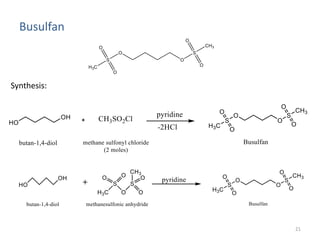
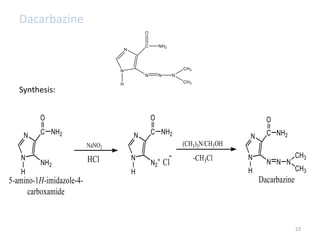
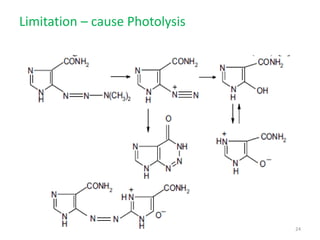
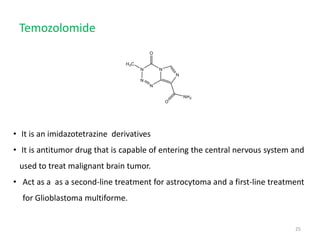
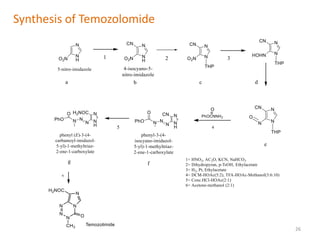
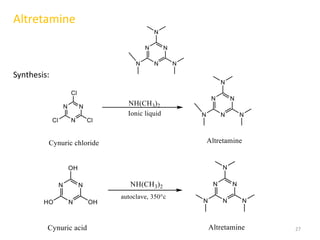
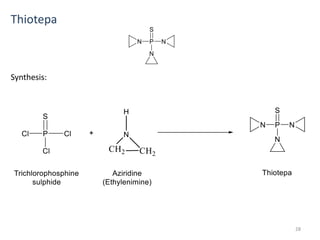
This document summarizes various alkylating agents used to treat cancer. It describes how alkylating agents work by forming covalent bonds with DNA to prevent replication. Specific agents discussed include nitrogen mustard, cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, melphalan, nitrosoureas like carmustine, alkyl sulfonates like busulfan, ethylenimines like dacarbazine, temozolomide, altretamine, and thiotepa. For many of these, the synthesis and mechanisms of action are outlined. Alkylating agents can cause adverse effects like myelosuppression, sterility, and increased leukemia risk.