K.Sailakshmi presented on degradation kinetics and mechanisms of drugs. She defined kinetics, order of reaction, and half-life. The presentation covered common degradation pathways like zero-order, first-order and second-order reactions. Mechanisms of drug degradation discussed included hydrolysis, decarboxylation, oxidation and photodegradation. Specific examples were provided to illustrate different degradation types and kinetics models. The presentation concluded that understanding degradation kinetics can provide insight into reaction mechanisms and improve product stability.







![8
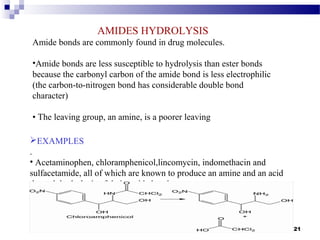
EXAMPLE:
Decomposition of NH3 in presence of molybdenum or tungsten is
a zero-order reaction. [Mo]
2NH3 → N2 + 3H2
The surface of the catalyst is almost completely covered by
NH3 molecules. The adsorption of gas on the surface cannot change by
the pressure or concentration of NH3. Thus, the concentration of gas
phase remains constant although the product is formed.Therefore, this
reaction zero order kinetics.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luucky-140929003340-phpapp02/85/Degradation-Kinetics-and-mechanisam-8-320.jpg)