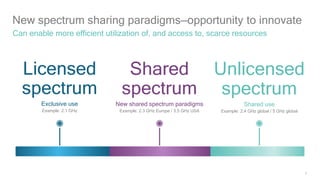
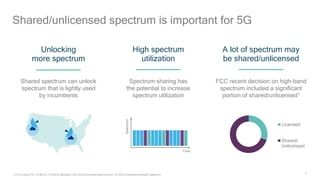
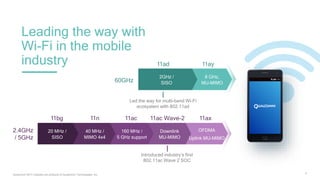
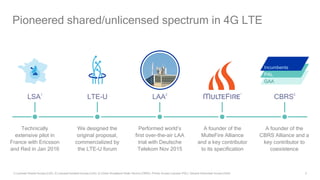
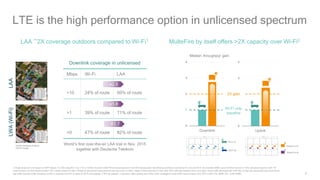
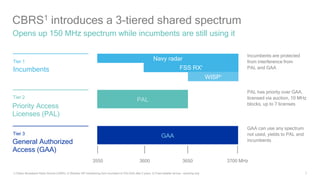
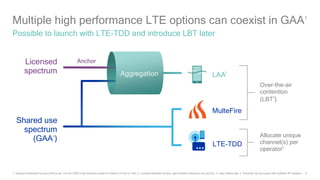
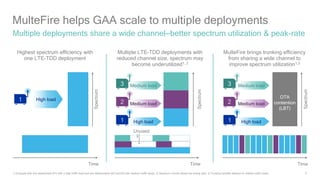
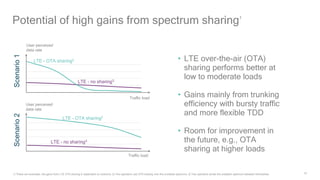
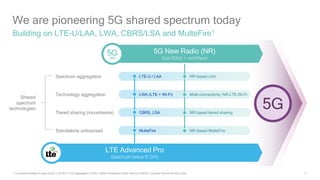
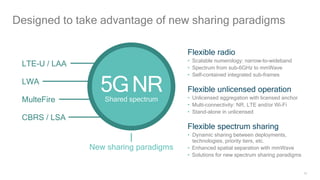
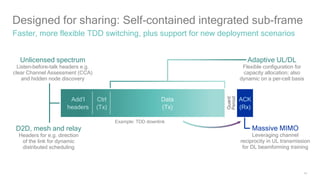
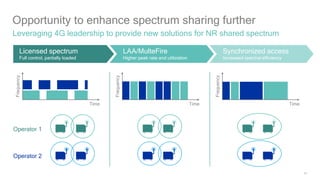
1) 5G shared spectrum technologies pioneered by Qualcomm such as LTE-U, LAA, LWA and MulteFire can unlock unused spectrum and improve spectrum utilization.
2) Qualcomm has contributed significantly to shared spectrum standards like CBRS and is a founder of alliances to develop shared spectrum technologies.
3) 5G New Radio is being designed by Qualcomm to support flexible deployment in shared, licensed, and unlicensed spectrum bands using technologies like LAA and MulteFire.