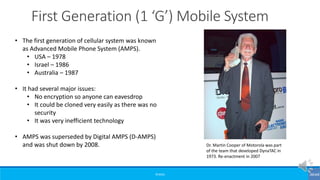
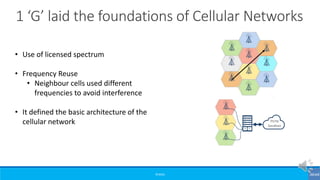
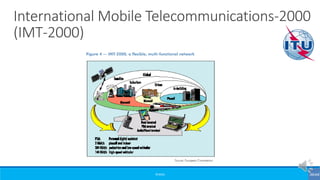
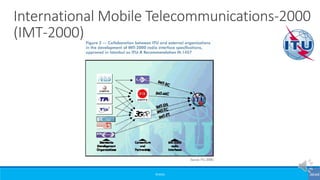
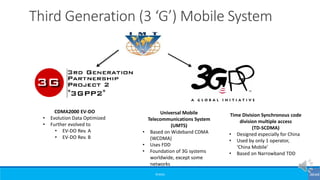
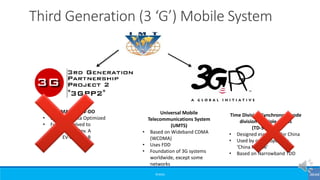
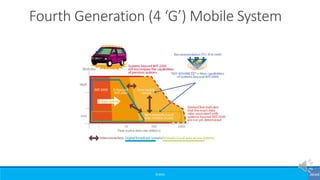
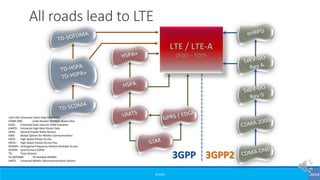
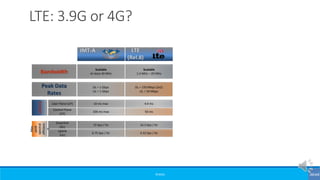
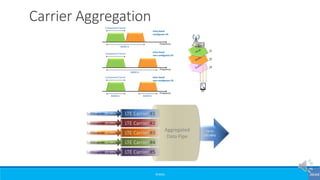
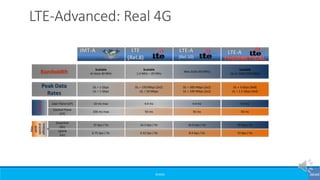
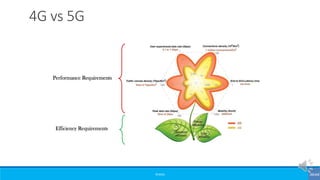
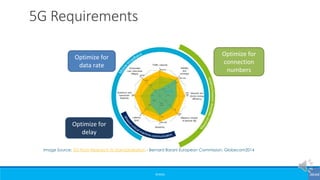
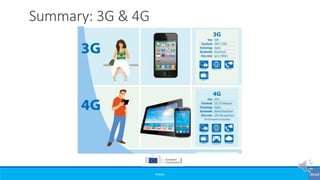
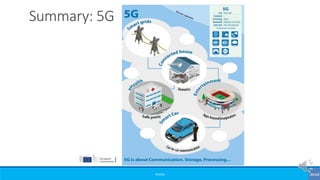
The document provides an overview of the evolution of mobile technologies from the introduction of mobile telephony in 1946 to the development of 5G. It outlines the key generations of mobile systems, detailing features, limitations, and advancements from 0G to 4G, including AMPS, GSM, and LTE. The document also compares the requirements and enhancements of 5G technology in relation to previous generations.