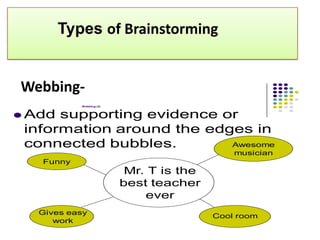
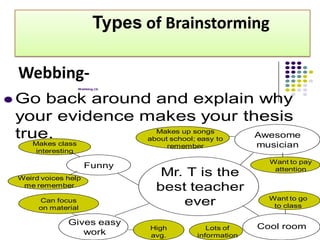
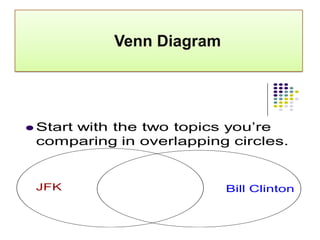
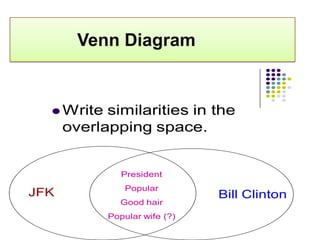
The document discusses various techniques for creative thinking such as focus groups, brainstorming, attribute analysis, synectics, and checklists of questions. It provides details on how each technique works, such as the rules and methods for brainstorming or the steps involved in attribute analysis. The overall goal is to develop creativity and help resolve problems through applying these different creative thinking techniques.