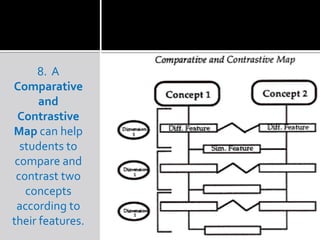
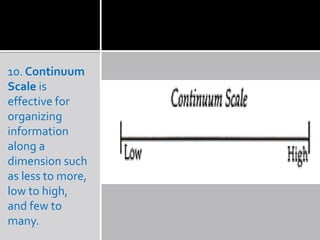
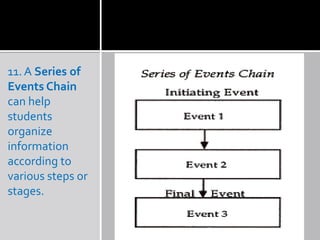
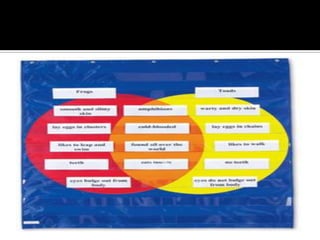
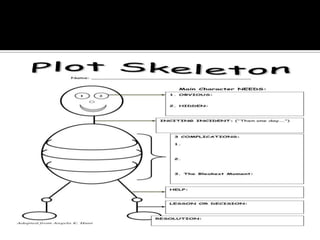
Graphic organizers are visual tools that help students organize information and ideas. They provide a visual representation of relationships between concepts. There are many different types of graphic organizers that can be used for different purposes, such as semantic webbing for organizing ideas in writing, network trees for hierarchical relationships, compare-contrast matrices for comparing attributes, and cycle maps for circular processes. The main purpose is to provide a visual aid to facilitate learning and instruction.