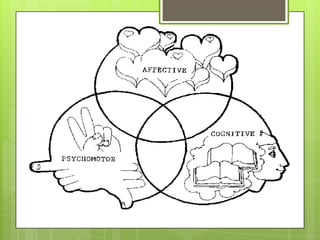
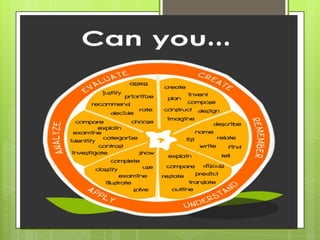
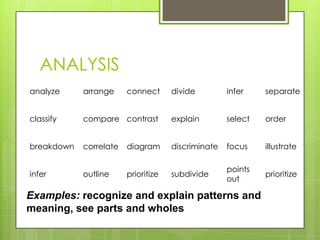
This document discusses critical thinking skills and their importance for students. It defines critical thinking as an active cognitive process used to identify assumptions, explore alternatives, and make decisions. The document outlines Bloom's taxonomy of cognitive domains - knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. It provides examples of how to develop these skills through activities that encourage logical thinking, reasoning, creative thinking, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The document emphasizes developing these skills is important for students to become independent thinkers who can make evidence-based decisions.