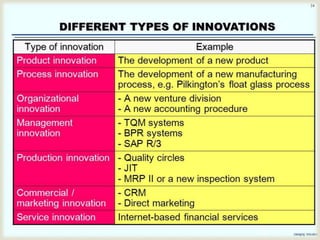
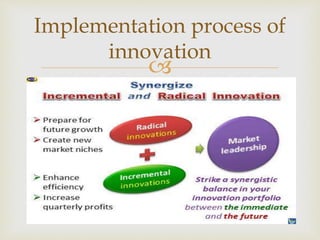
The document discusses the concept of innovation as the introduction of new methods, products, or processes to create value for firms and consumers. It distinguishes between innovation and invention, highlighting that innovation requires a commercial application alongside creativity, iteration, and handling of failures. Various types of innovation are explored, including product, process, and service innovation, alongside the phases of design and implementation.