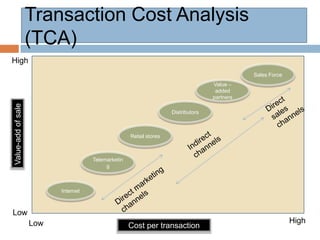
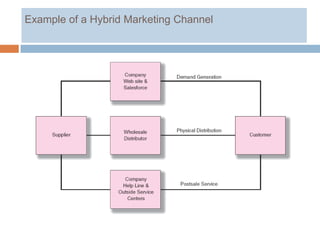
1) Marketing channels exist to perform needed functions like distribution at lower cost than if a customer or manufacturer acted alone.
2) When designing distribution channels, key objectives include increasing product availability, satisfying customer service needs, ensuring promotional support, obtaining market information, maintaining cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
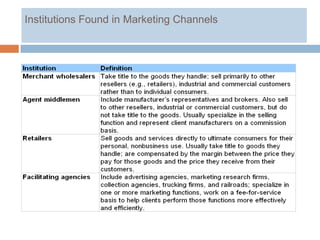
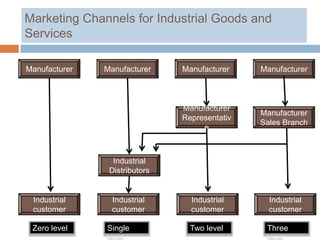
3) Common institutions in marketing channels include merchant wholesalers, agents, retailers and non-store retailers. The best alternative depends on the priorities around these objectives and a company's competitive strategy.