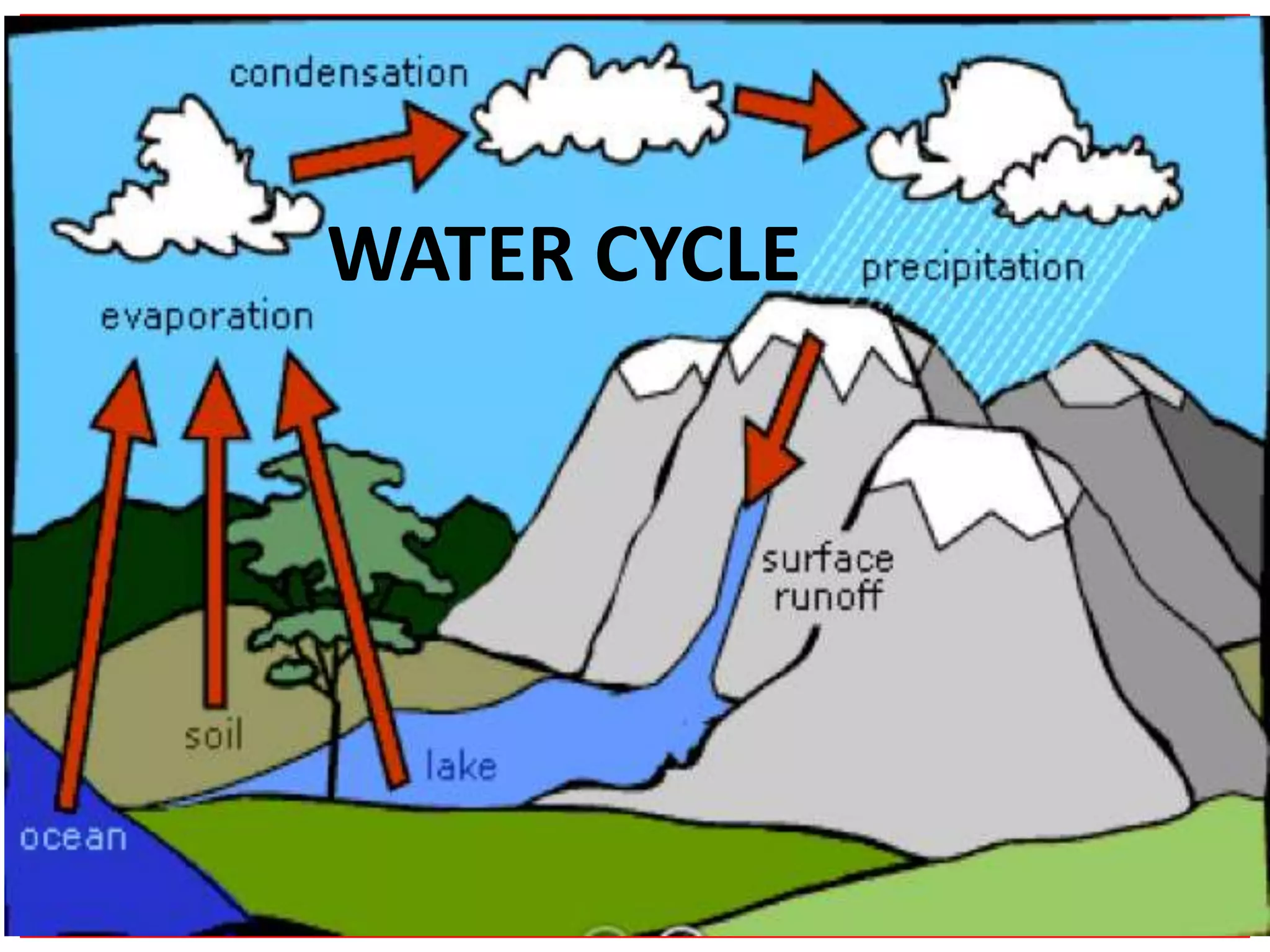
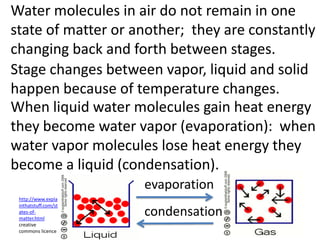
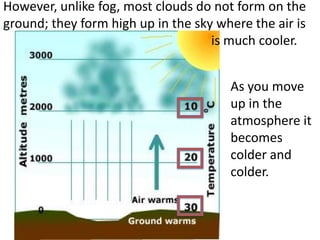
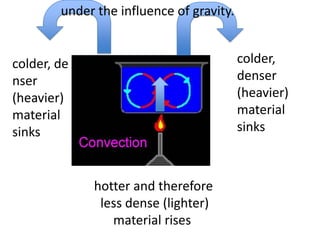
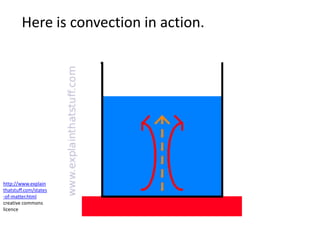
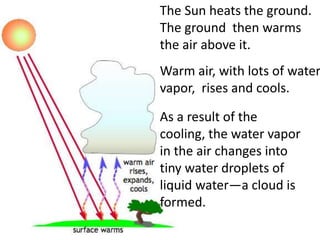
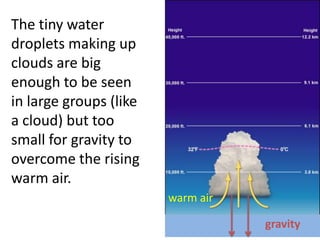
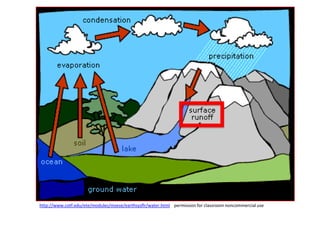
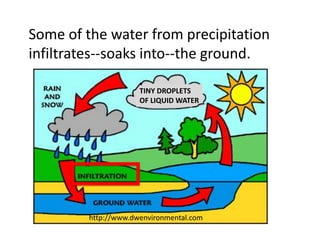
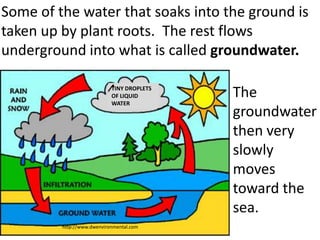
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and other bodies of water into water vapor in the air. Warm air containing water vapor rises and cools, condensing into clouds. Water then falls back to Earth's surface as precipitation like rain or snow. Some precipitation runs over land as surface water toward rivers and lakes, while other precipitation soaks into the ground as groundwater. This completes the cycle as infiltrated water returns to bodies of water through subsurface flow.