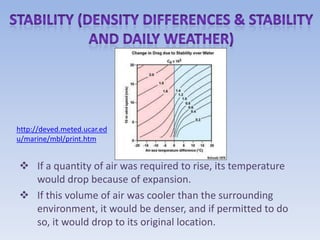
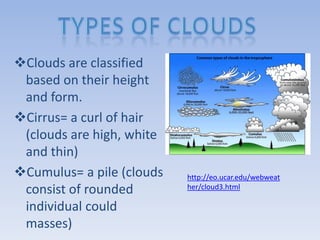
When air rises and expands, it cools through adiabatic processes. This cooling can cause water vapor in the air to condense into clouds and precipitate out as rain, snow, sleet or hail depending on temperature levels. Clouds are classified based on their height and physical structure into cirrus, altostratus and nimbostratus clouds that form at high, middle and low altitudes respectively.