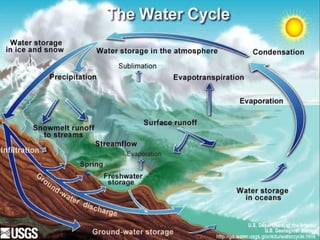
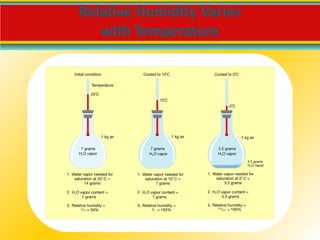
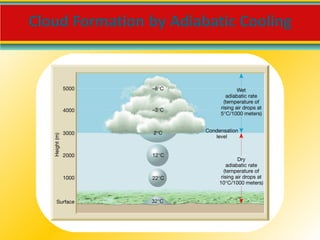
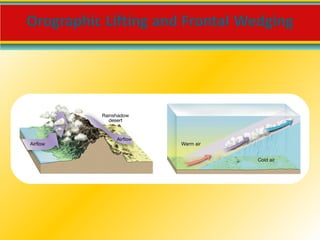
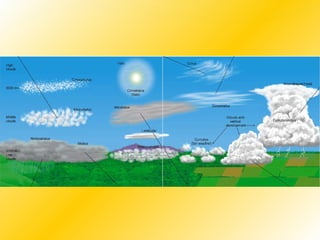
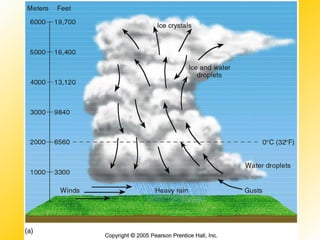
Water vapor is the most important gas in the atmosphere and is the source of all condensation and precipitation. The water cycle begins with evaporation and includes condensation, precipitation, and water running off or sinking into the ground. Clouds are classified based on their height and form, with cirrus, cumulus and stratus being the main cloud types located in the high, middle and low levels of the atmosphere respectively. For precipitation to form, cloud droplets must grow substantially through processes like collision-coalescence in warm clouds and the Bergeron process in cold clouds. The type of precipitation reaching the surface depends on the temperature profile in the lower atmosphere.