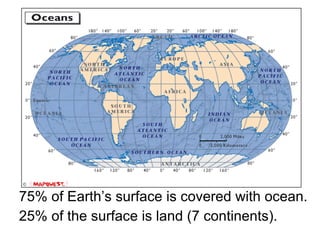
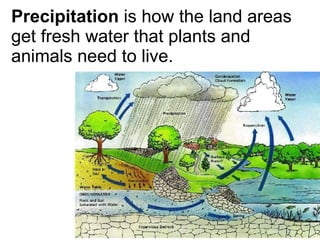
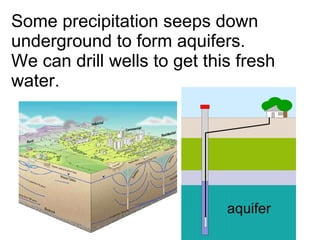
The document discusses the water cycle and the different states of water. It explains that 75% of the Earth's surface is covered by oceans, which contain 97% of the planet's water in the form of salt water. The remaining 3% is fresh water, found in rivers, lakes, glaciers, and underground. The water cycle involves evaporation of water from oceans and land into vapor, which rises into the atmosphere and condenses to form clouds. Precipitation occurs when the water falls as rain or snow to the ground, where some soaks into the soil and some runs off into rivers and lakes, eventually making its way back to the oceans to repeat the cycle.