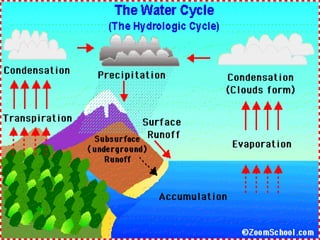
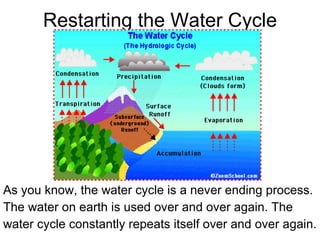
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It involves six main processes: evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, surface runoff, and accumulation. Evaporation turns water from oceans, rivers, and lakes into vapor, and transpiration occurs when water evaporates from plants. Condensation occurs when water vapor in the air cools and turns back into a liquid in clouds. Precipitation results when clouds become too heavy and water falls as rain, snow, sleet or hail. Surface runoff transports precipitation from land to streams and rivers. Accumulation occurs when water flows into oceans, lakes, and seas, restarting the cycle.