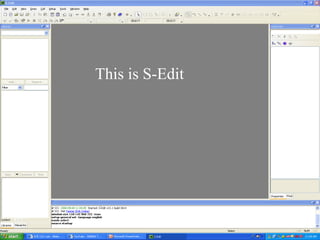
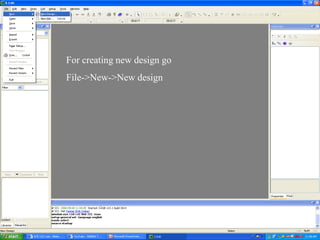
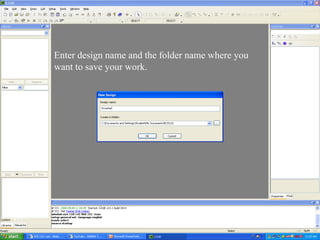
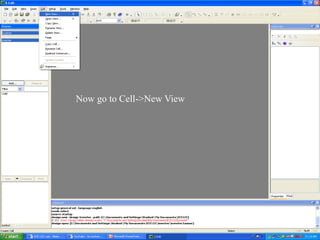
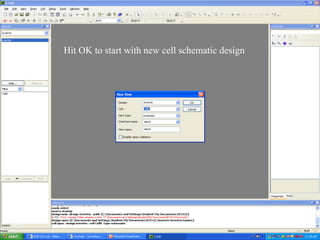
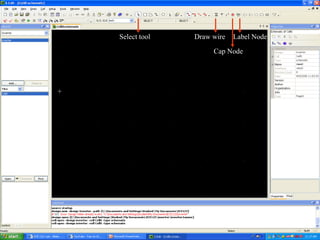
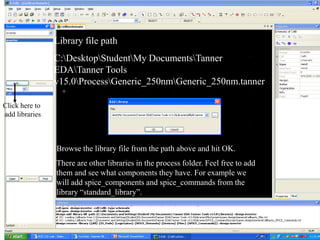
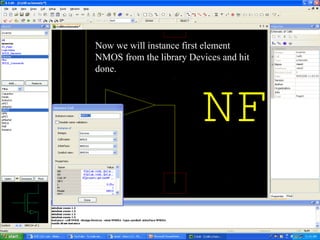
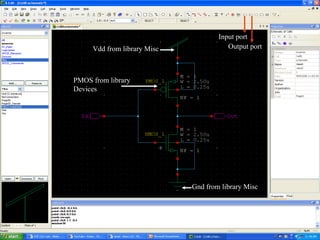
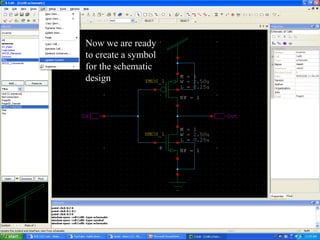
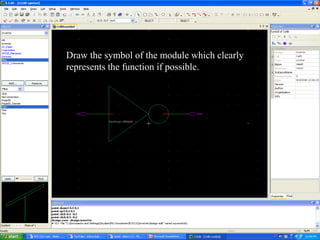
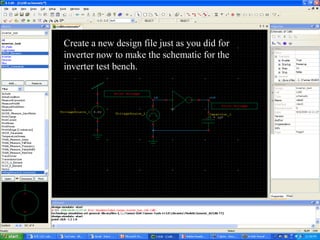
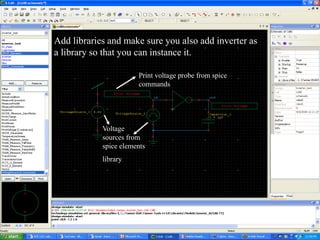
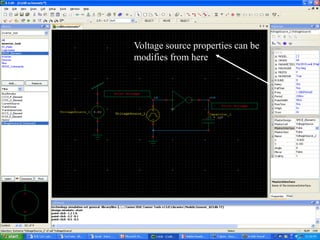
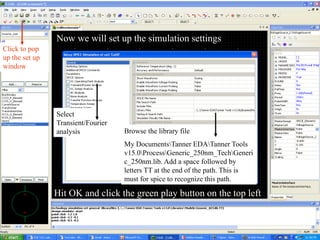
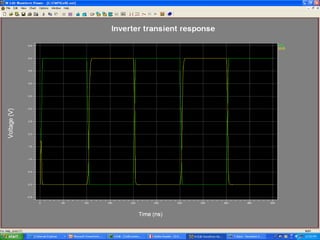
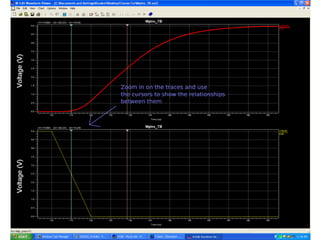
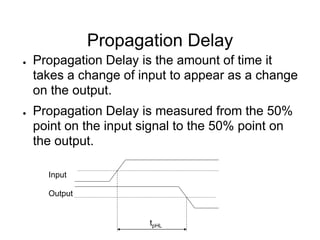
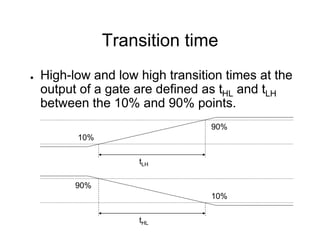
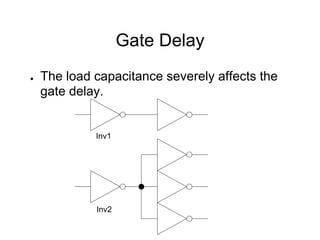
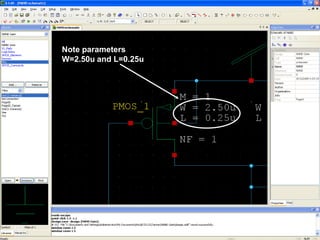
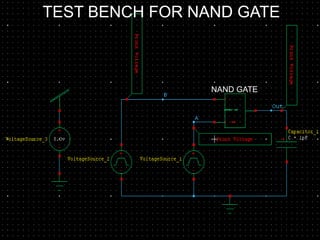
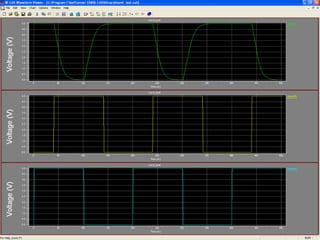
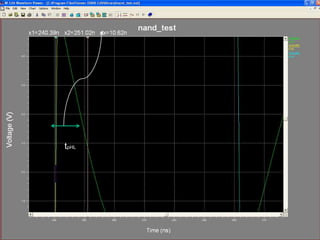
This document provides an overview of using Tanner Tools for digital circuit design and simulation. It discusses the objectives of using Tanner Tools, which includes getting experience with design, simulation, and layout of digital logic circuits. It then describes the key components of Tanner Tools, including L-Edit for layout, S-Edit for schematic entry, and T-Spice for simulation. The document walks through creating a basic inverter design in S-Edit, setting up a test bench simulation, and analyzing the output waveform to determine propagation delay. It also discusses best practices for file organization and management when using Tanner Tools.