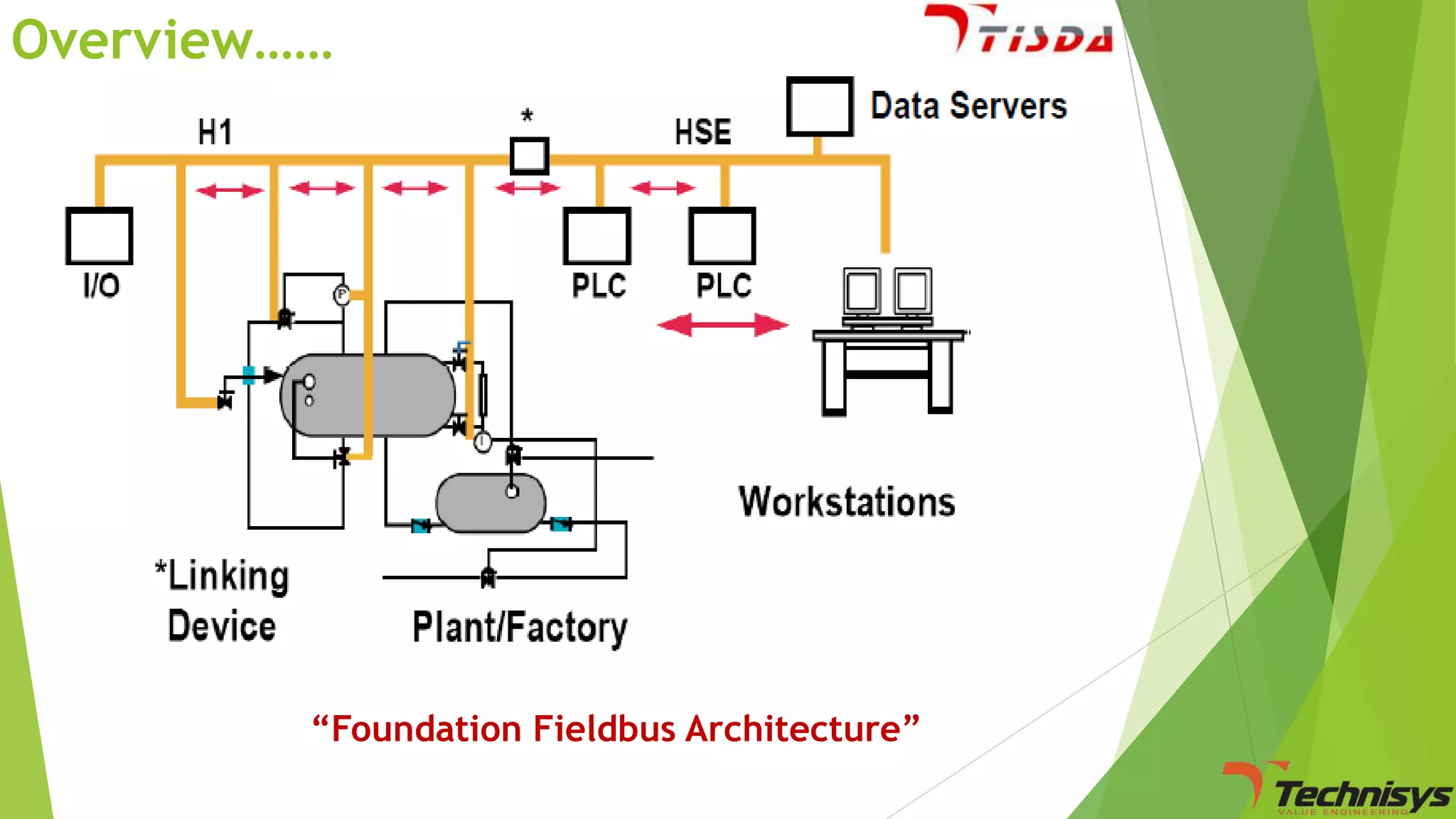
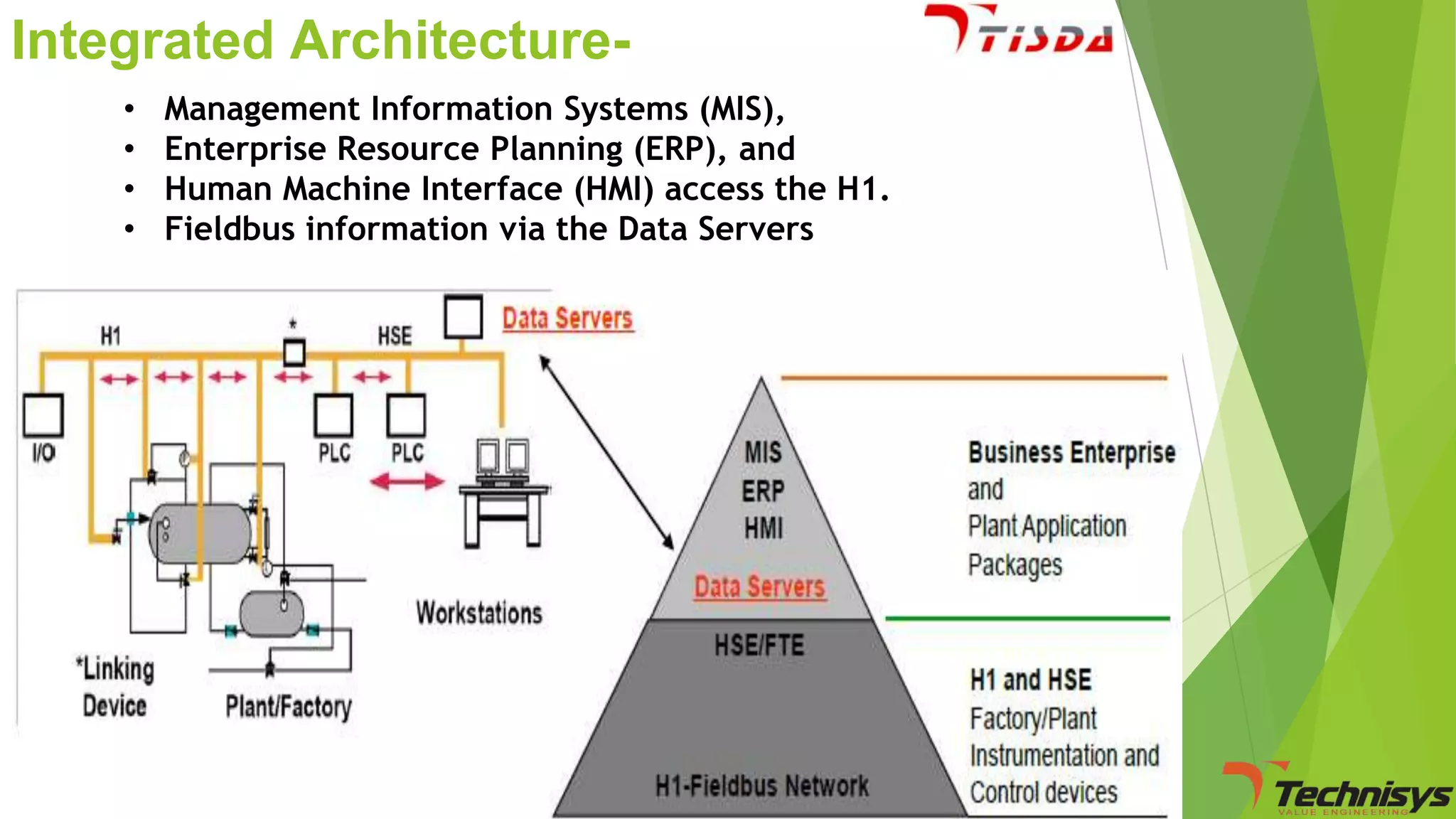
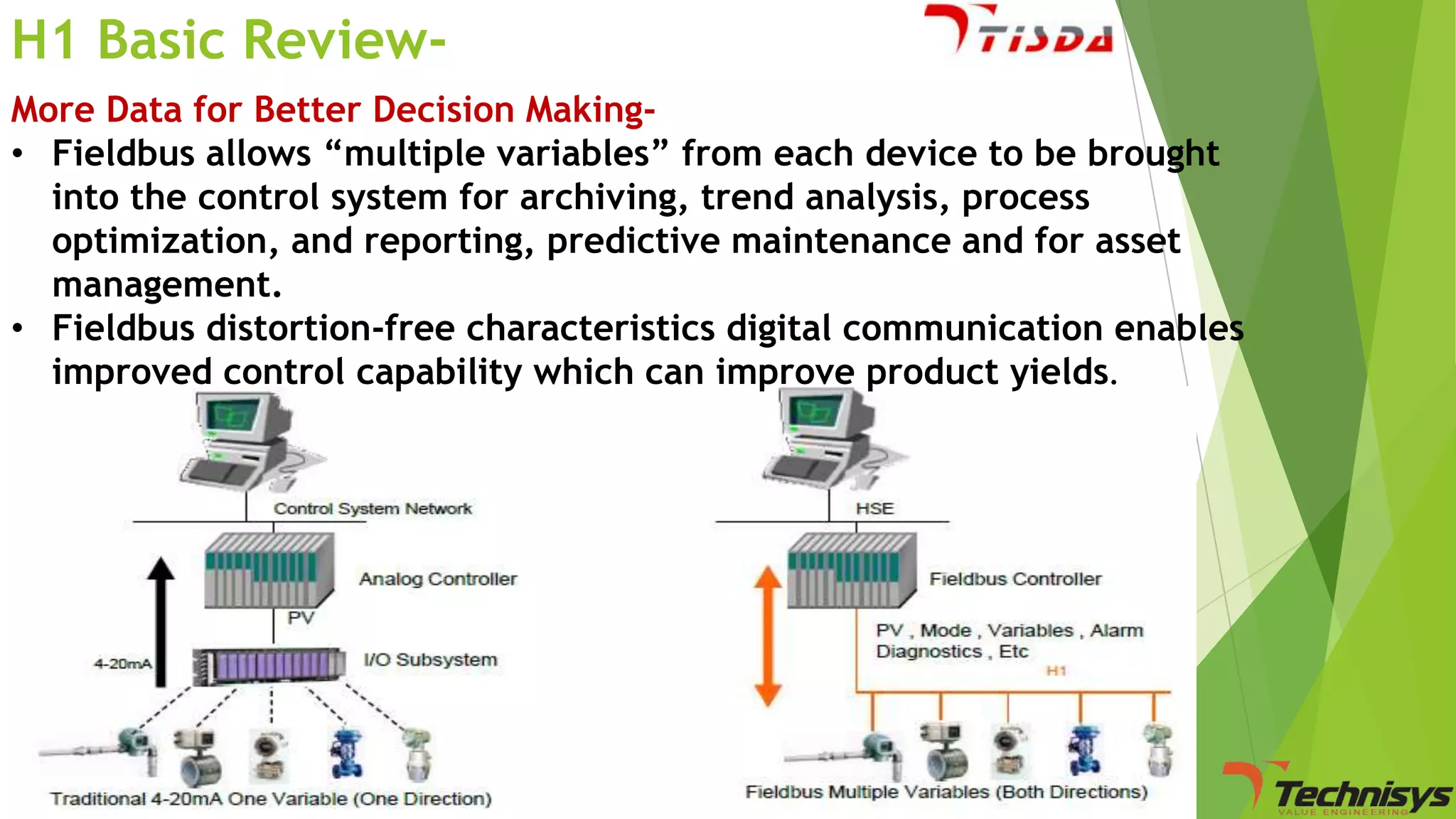
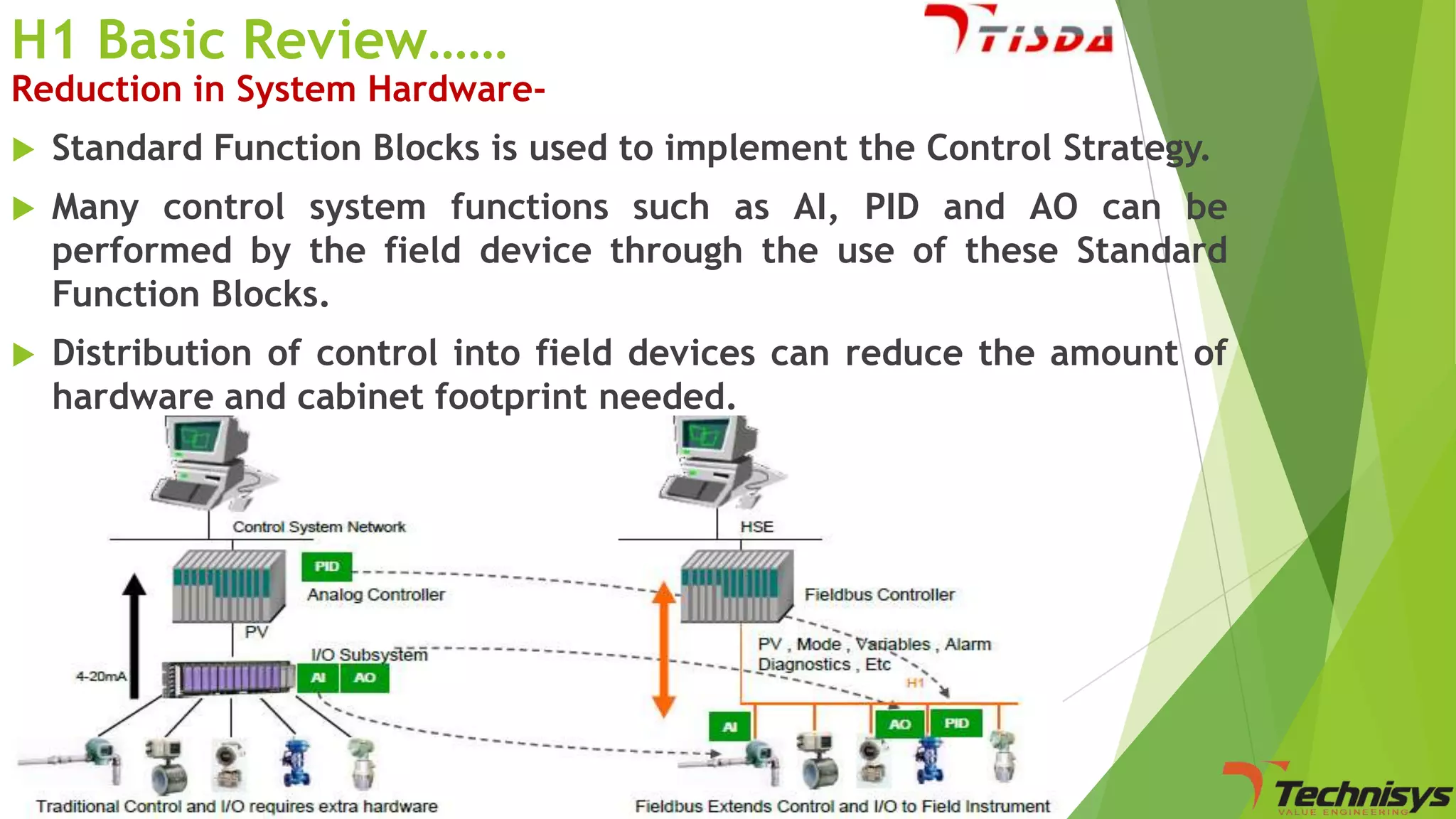
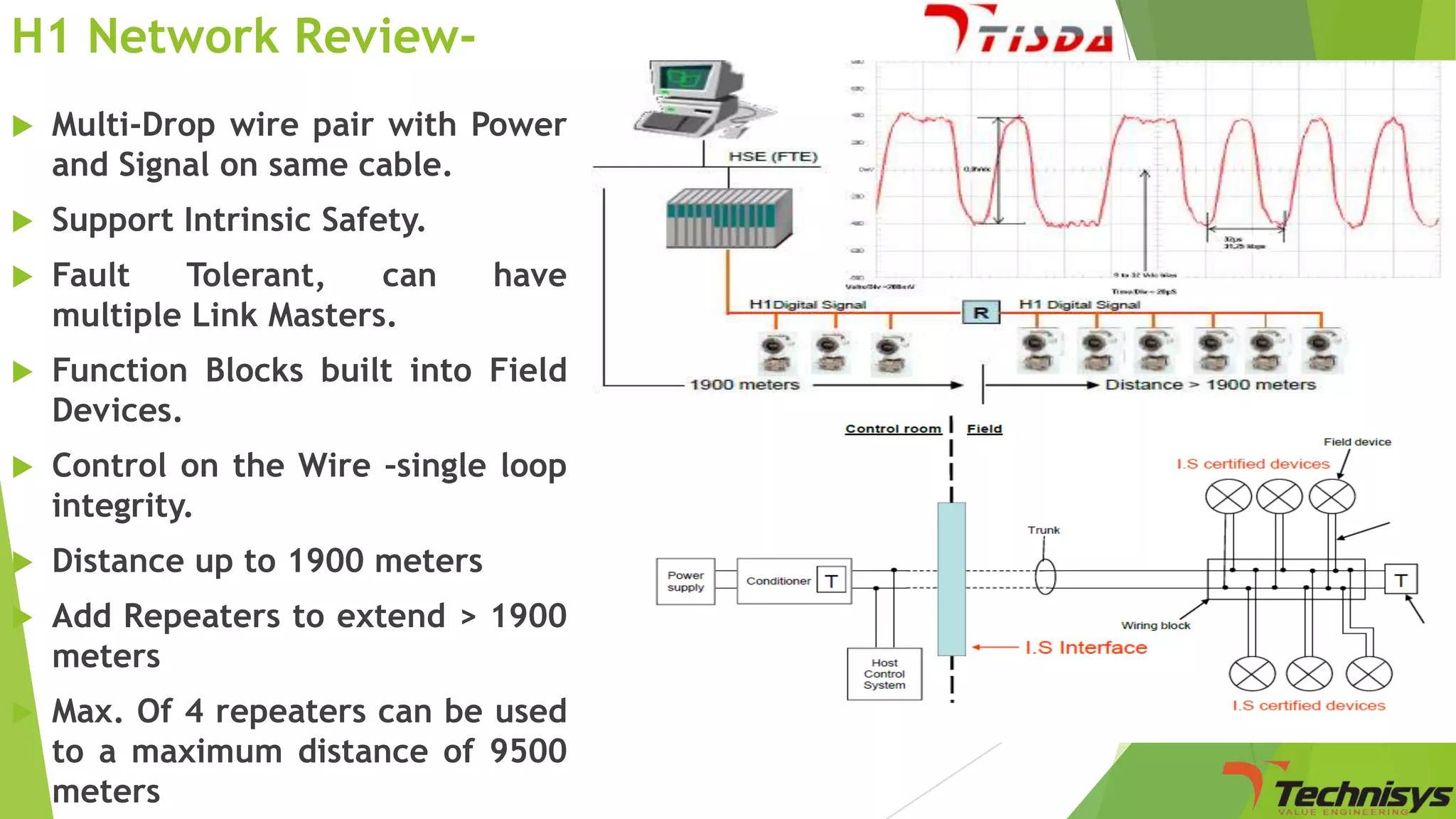
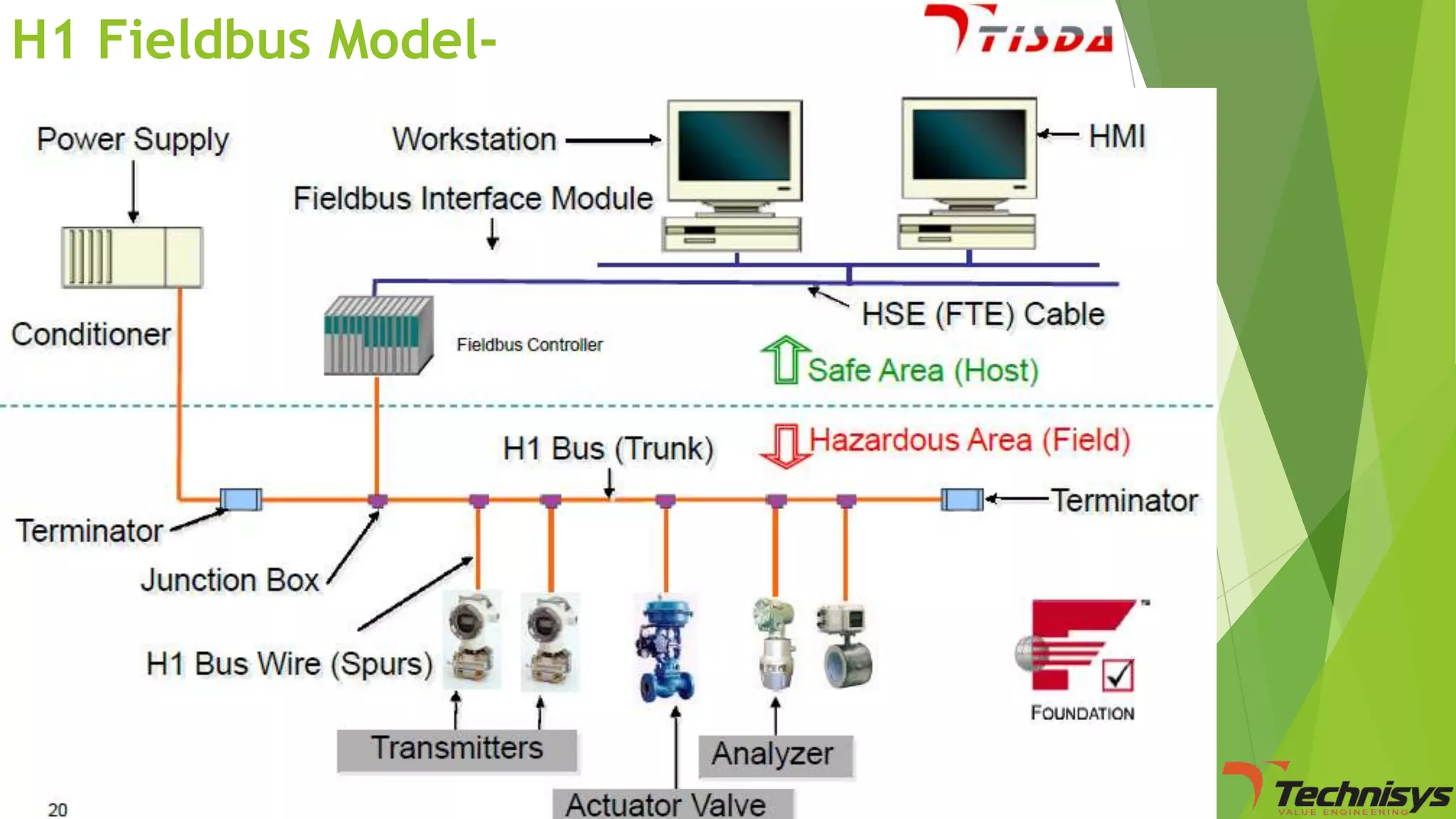
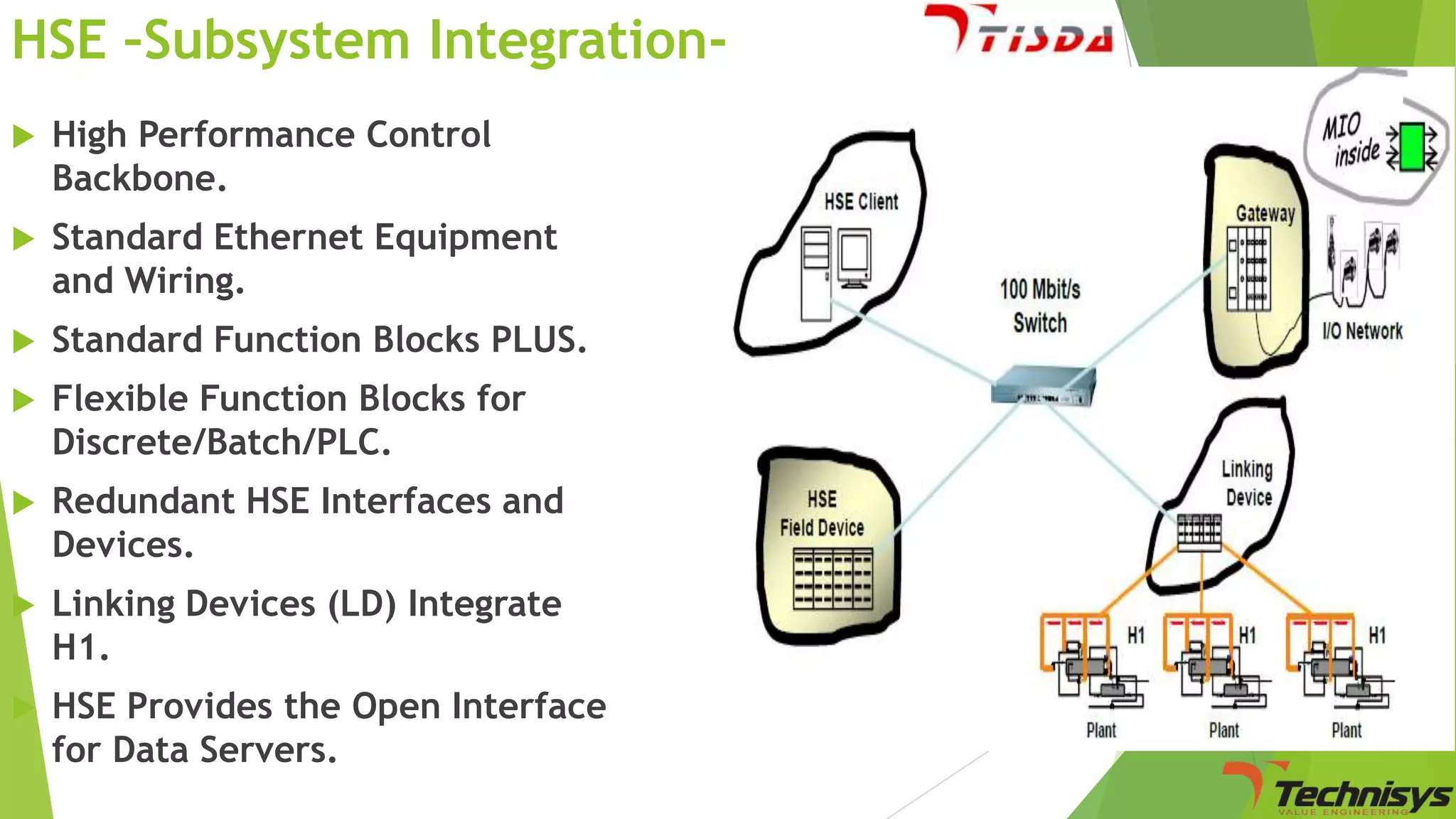
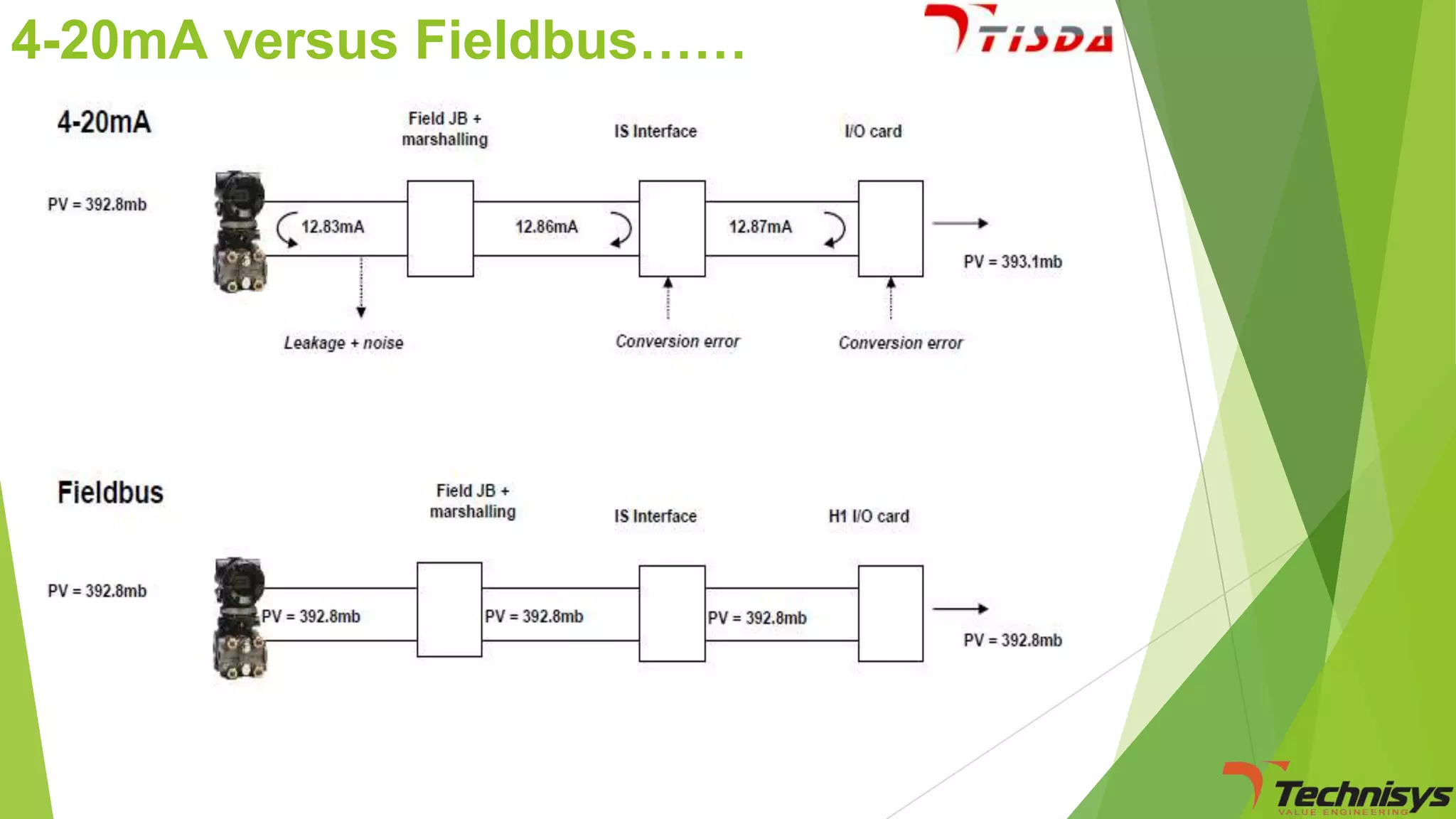
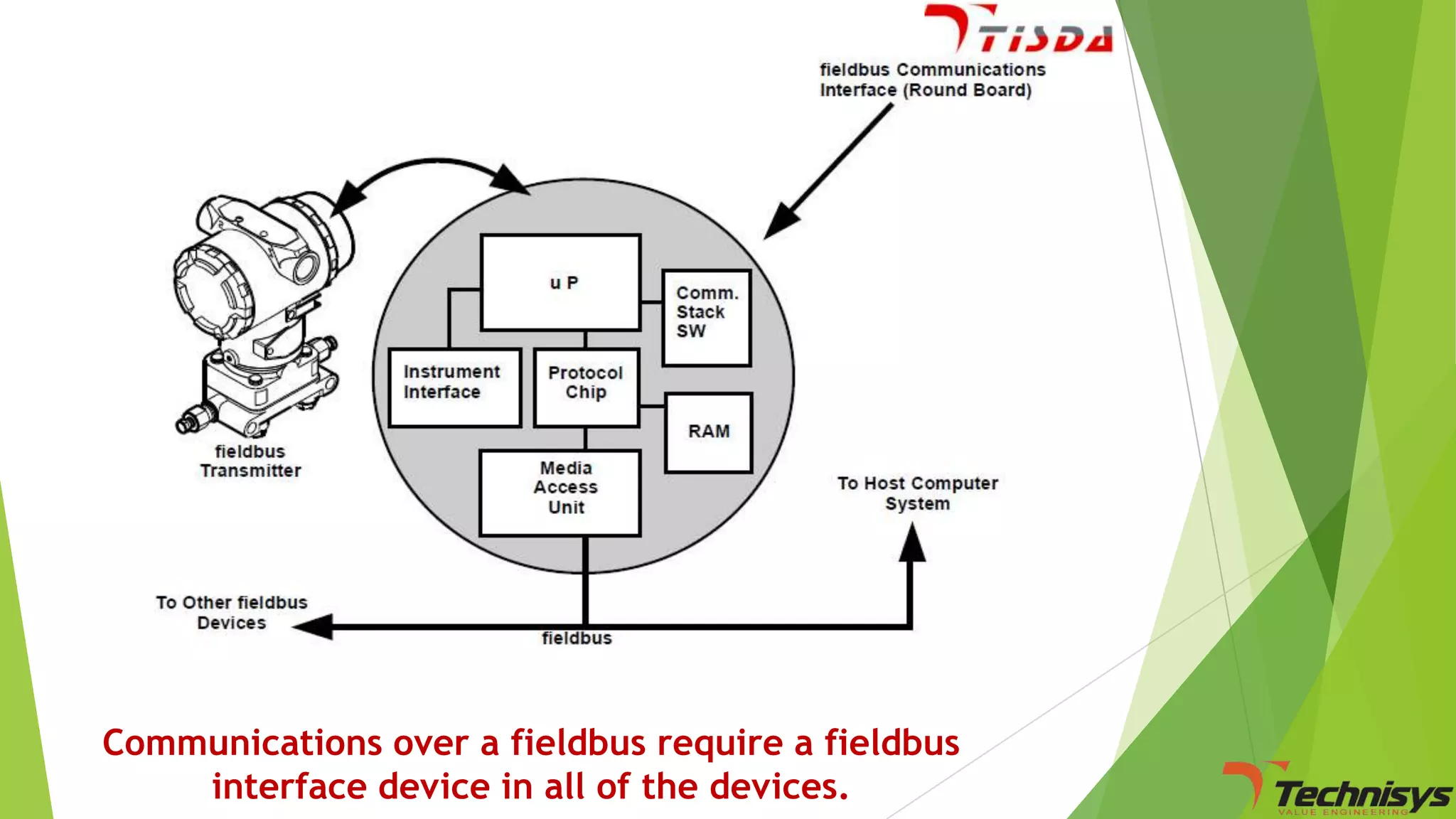
Fieldbus is a digital communication network that replaces the existing 4-20 mA analog standard. It uses a bi-directional, multi-drop, serial-bus network to connect field devices like sensors, actuators, and controllers. Foundation fieldbus is an open architecture that uses digital communication over two wire pairs to connect intelligent field devices and distribute control applications across the network. It provides benefits like reduced wiring, self-diagnostics, improved control capability, and integration with information systems. While fieldbus offers advantages in cost savings and performance, it also has some disadvantages like increased complexity, higher component costs, and risks around standards.