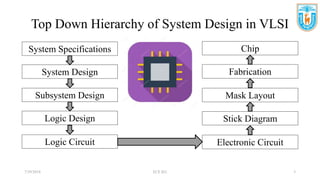
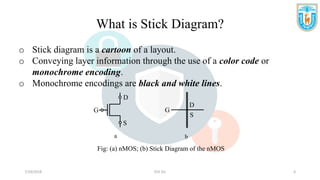
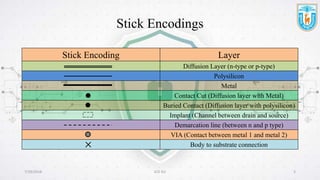
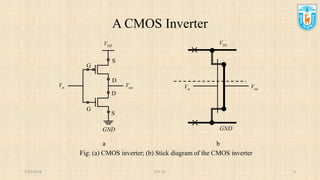
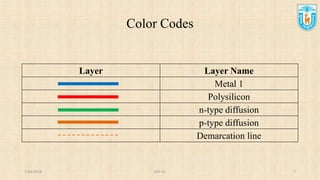
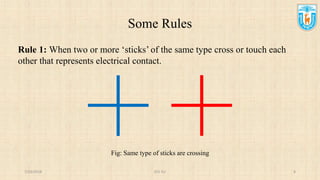
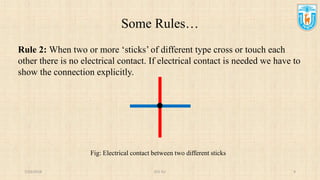
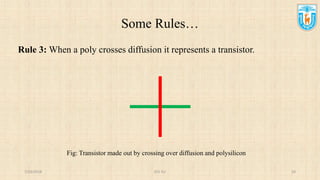
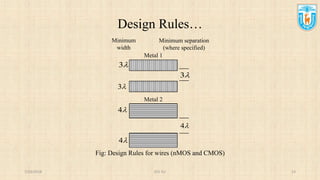
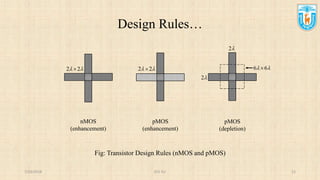
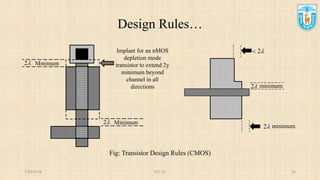
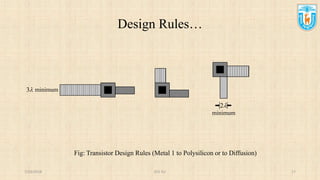
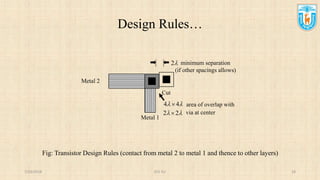
This presentation discusses stick diagrams and lambda-based design rules for VLSI system design. It begins with an overview of the top-down design hierarchy and then defines stick diagrams as a way to represent different layers of a layout using colors or monochrome lines. Common stick encodings are presented along with examples of drawing a CMOS inverter. Design rules are then covered, with lambda serving as a size-independent unit and rules specifying dimensions for wires, transistors, and contacts between layers. The goal is to convey key layer information and spacing requirements for mask layouts in a standardized way.