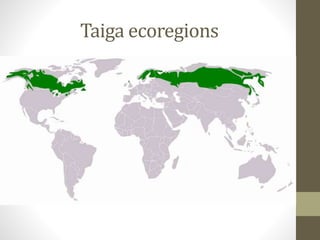
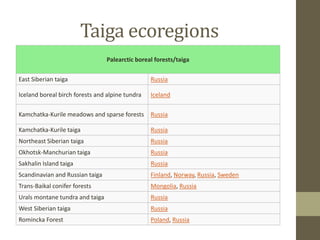
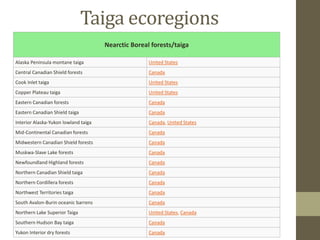
This document discusses the taiga biome, also known as boreal forest or snow forest. The taiga is characterized by coniferous forests of pines, spruces and larches, and is found at high latitudes across northern Europe and Asia as well as parts of North America. It has a subarctic climate with short summers and long, cold winters. The soil of the taiga is young, thin, acidic and low in nutrients. Wildfire is a natural disturbance that shapes the composition and development of boreal forest stands, occurring every 50-200 years on average. The taiga biome faces threats from human activities, climate change, insects and pollution.