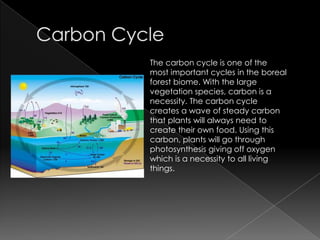
The boreal forest, or taiga, is primarily composed of coniferous trees and spans a continuous belt from North America to Eurasia, characterized by a unique ecosystem influenced by water, nitrogen, and carbon cycles. Natural disasters like earthquakes can significantly disrupt this biome, leading to habitat destruction and the loss of animal populations, followed by a period of secondary succession where new plant life begins to regrow. The role of decomposing organisms and scavengers is crucial in restoring the ecosystem by providing nutrients and aiding the spread of seeds.