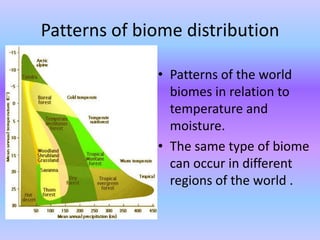
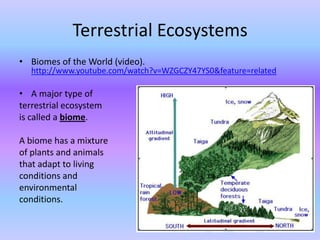
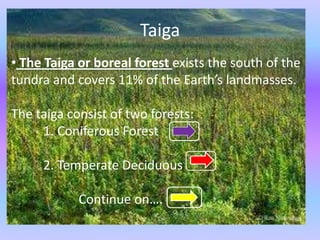
The document discusses the biosphere and its major biomes. It describes how ecosystems were originally distributed based on climate and how each biome has adapted to different environmental conditions. It then provides details on several major biomes: tundra, taiga, coniferous and deciduous forests, tropical forests, and deserts. For each biome it highlights the location, climate, dominant plant and animal species, and key adaptations for survival.