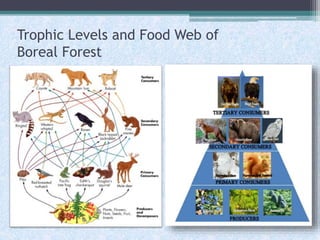
The boreal forest has long, cold winters and short, mild summers, with average yearly temperatures below freezing. The soil is acidic and nutrient-poor, and the ground is often swampy. Coniferous trees like firs and pines dominate the vegetation and have adaptations for cold tolerance. Large herbivores include moose and elk, and predators include lynx and bobcats. Precipitation falls mainly as snow in winter, and the long summer days allow a brief growing season for plants. Boreal forests circle the northern hemispheres of North America and Eurasia.