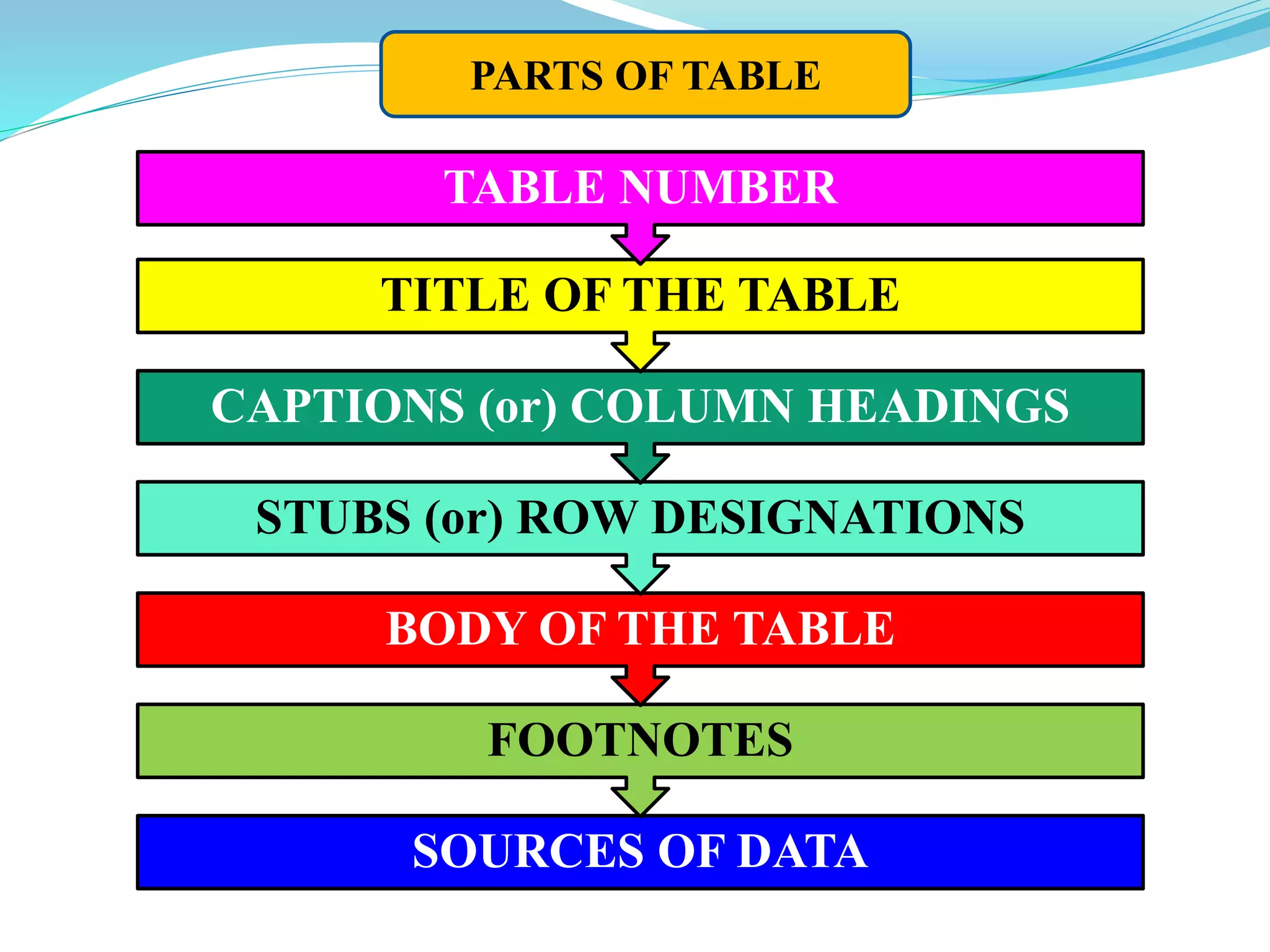
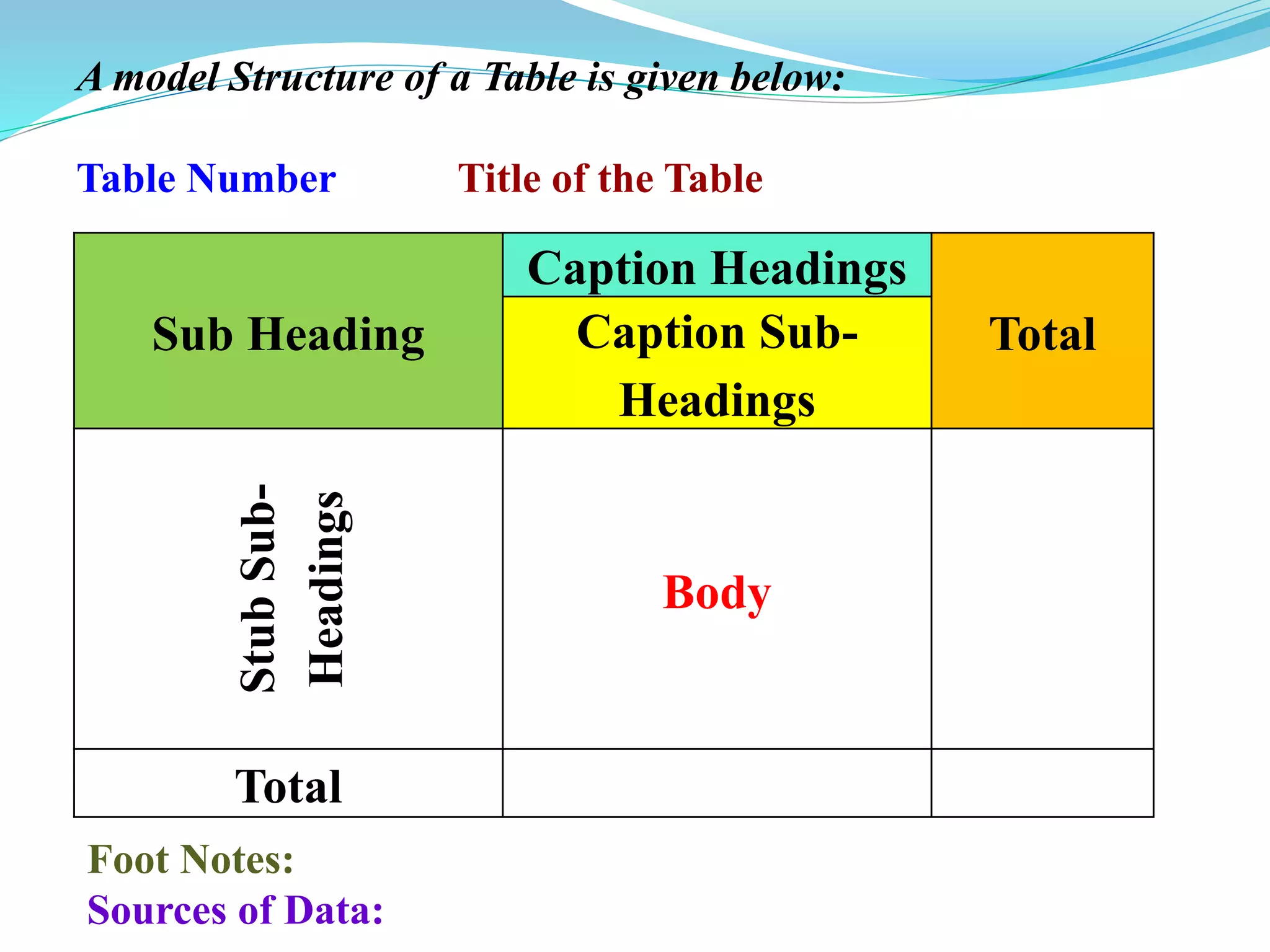
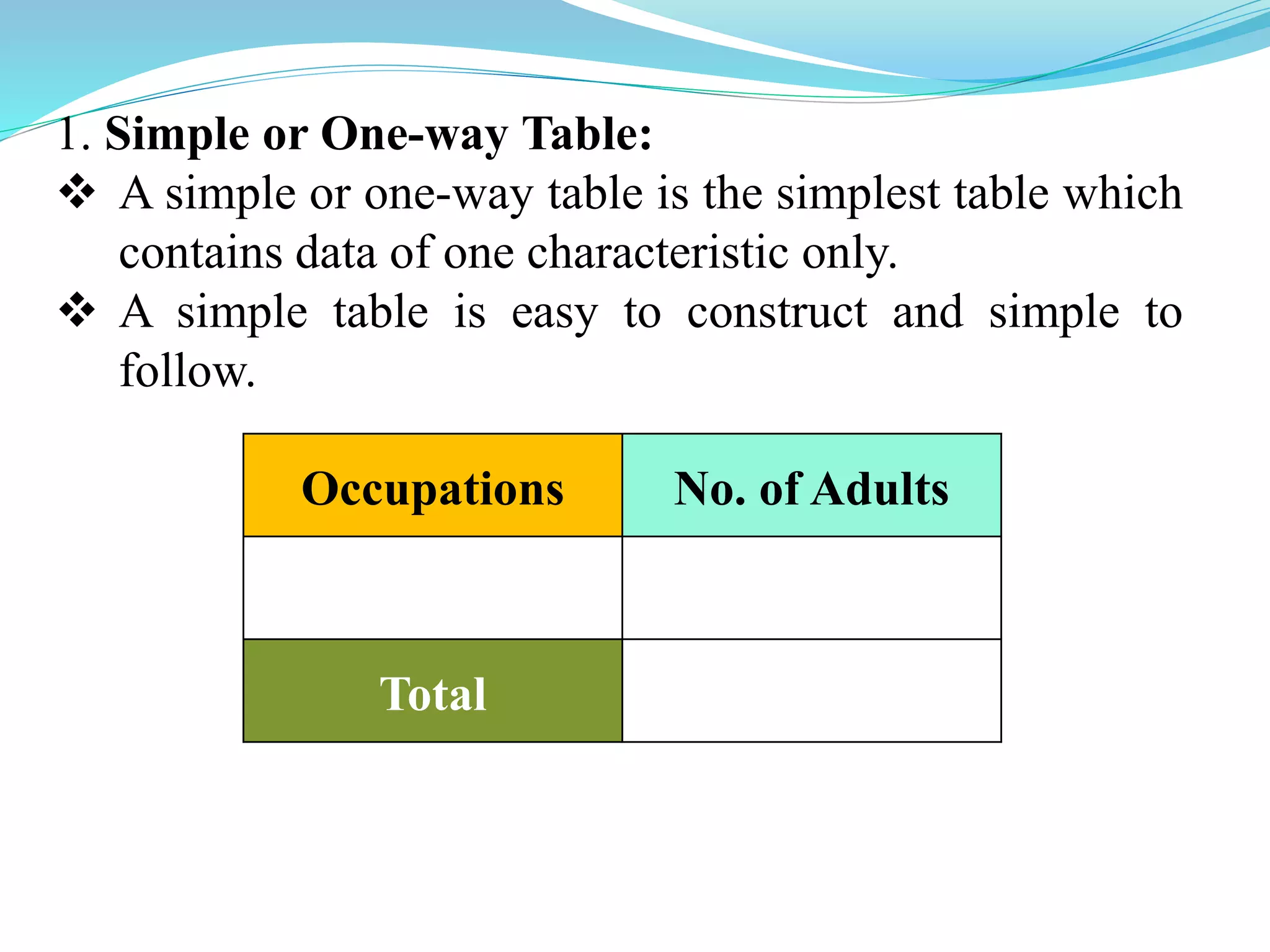
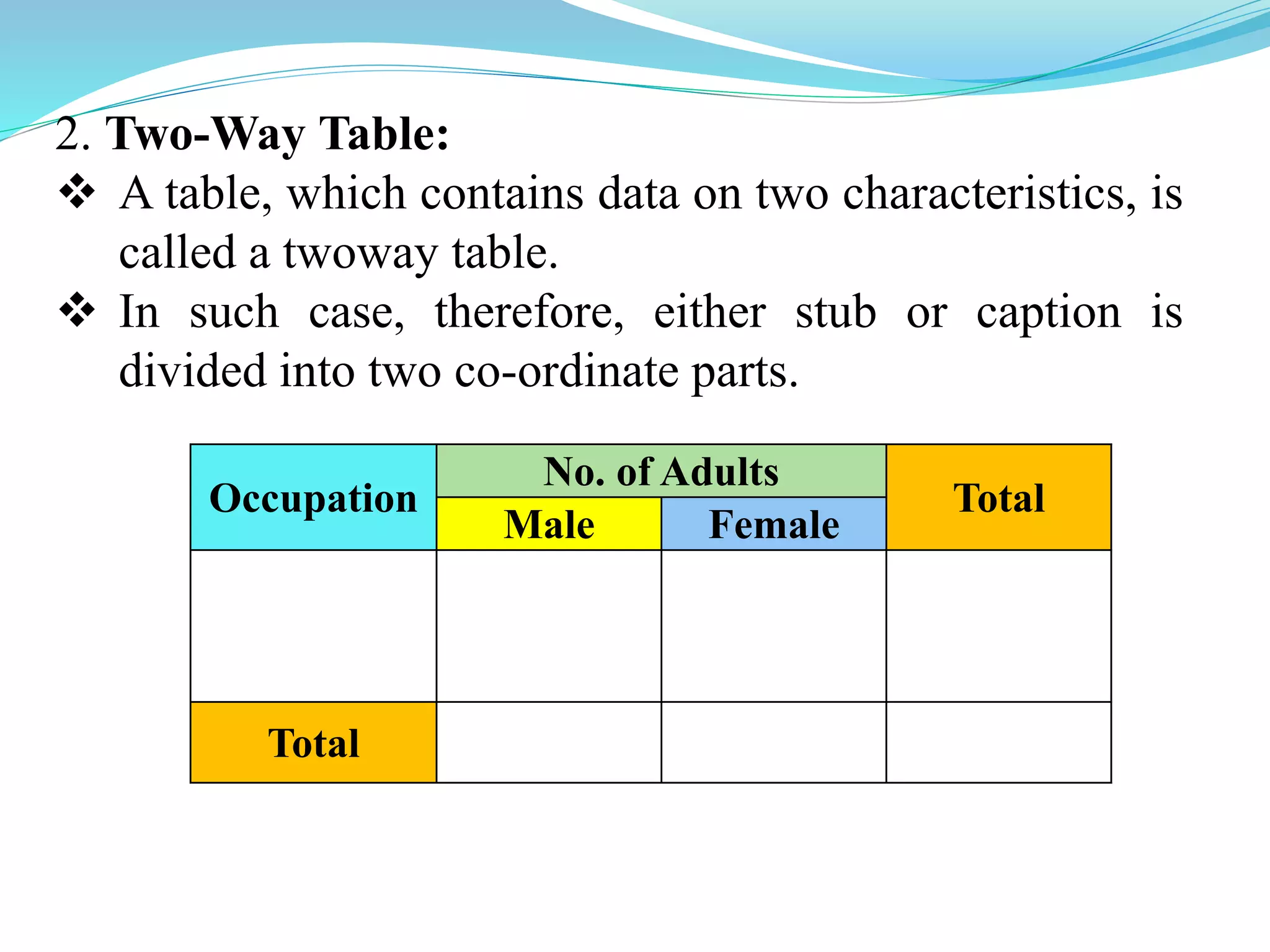
This document discusses tabulation, which is the logical presentation of numerical data in rows and columns to simplify presentation and facilitate comparisons. It defines tabulation and lists its advantages. It also describes the different types of tabulation (simple, complex), parts of a table (number, title, captions, stubs, body, footnotes, sources), and types of tables (simple/one-way, two-way, manifold). Merits include presenting complex data clearly and compactly while facilitating comparisons, and demerits are limitations on qualitative data and description.