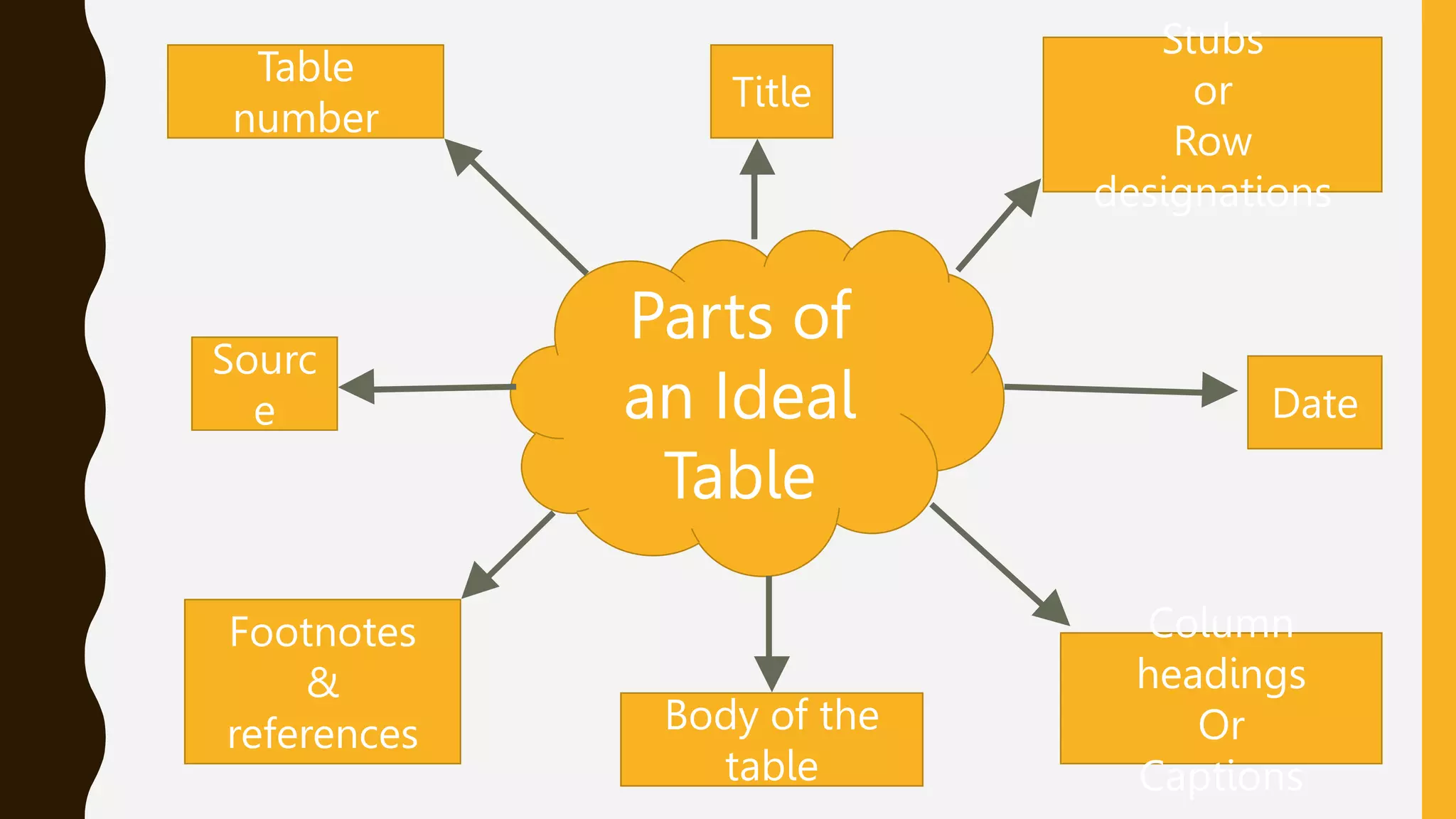
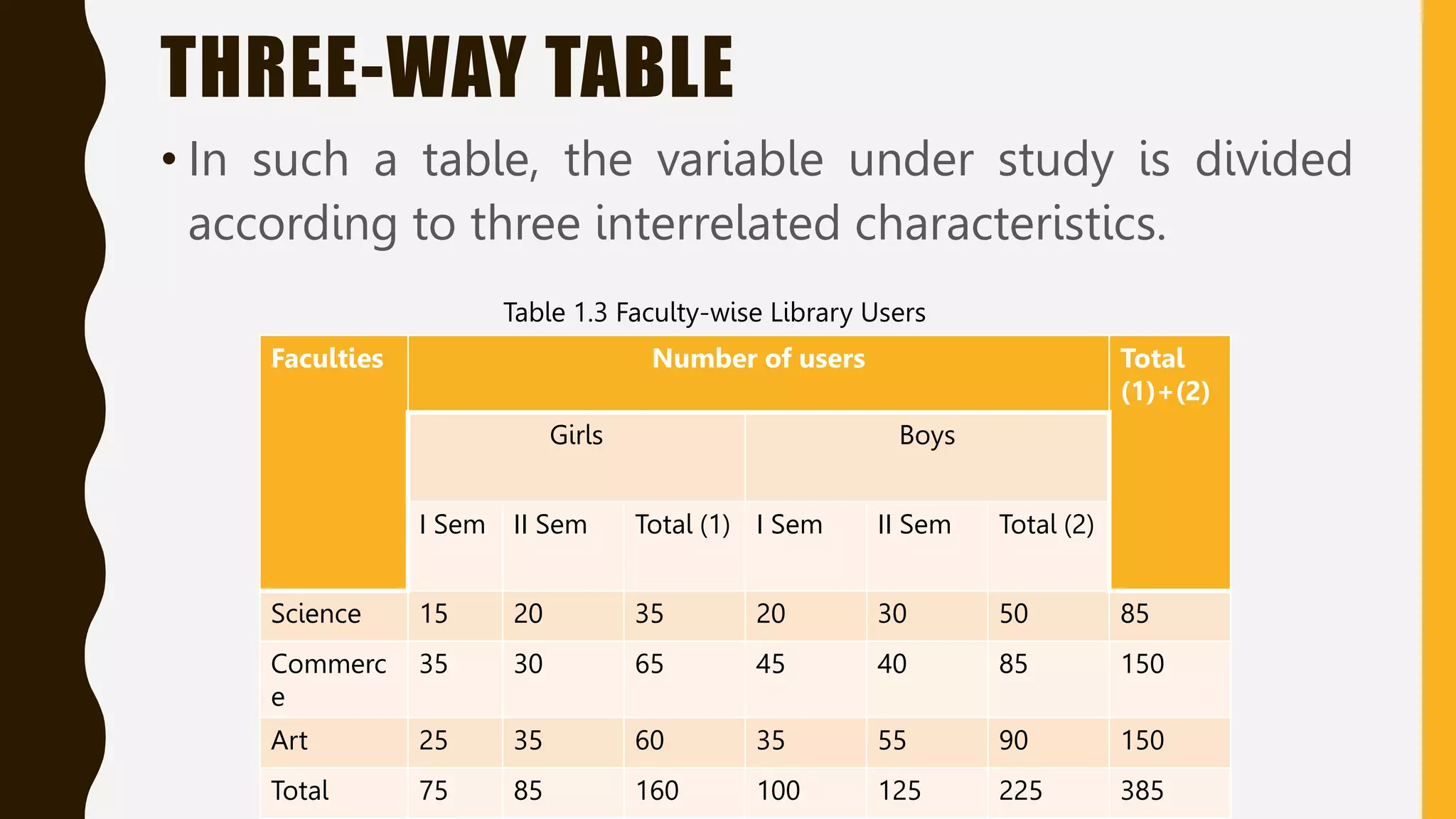
This document discusses different methods of organizing and presenting data in tables. It defines what a table is, the objectives and rules of tabulation, and the key parts of an ideal table. It also describes the importance of tabulation and different types of tables including simple, complex, double, and manifold tables. Tabulation is presented as a systematic way to organize data using rows and columns to facilitate analysis and interpretation.