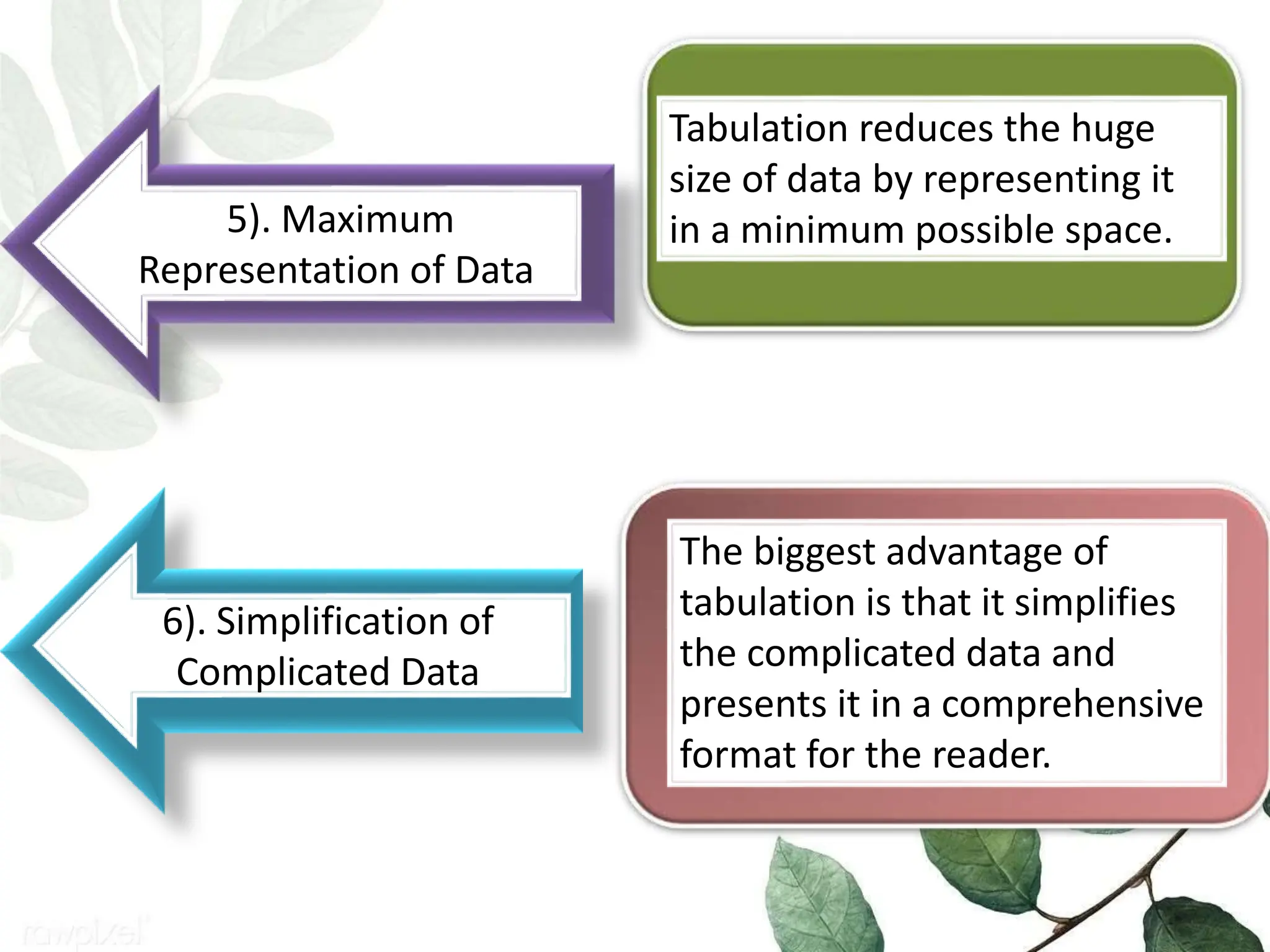
The document discusses tabulation, which is presenting data in tables to interpret results easily. It describes characteristics of good tables, types of tables including simple, complex, and multi-way tables. Rules of tabulation include title, size, structure. Significance is that tables allow easy data comparison, analysis, and detect missing data. Tabulation simplifies complicated data and maximizes data representation in minimal space.