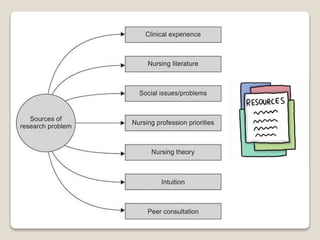
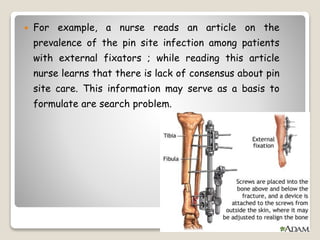
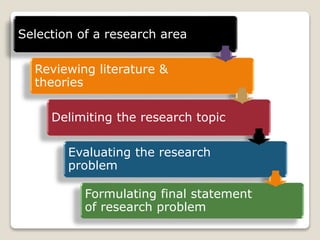
This document discusses the identification and formulation of research problems. It begins by defining a research problem and noting that identifying a problem is the first step of the research process. It then discusses several potential sources that a research problem may come from, such as personal/practical experiences, literature reviews, previous research, theories, and social issues. The document also outlines criteria for selecting a good research problem, including significance, originality, feasibility, being solvable, being current, and being interesting to the researcher. It concludes by outlining the process of formulating a research problem from selecting a broad topic area to delimiting the topic and evaluating and stating the problem.