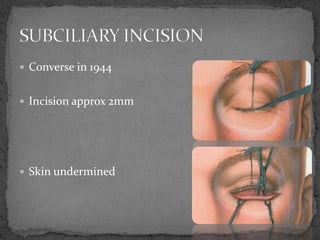
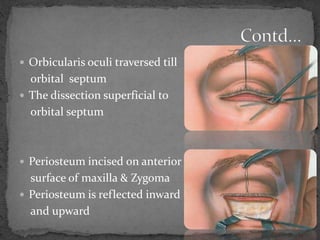
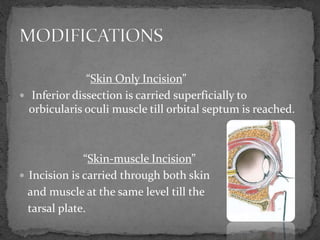
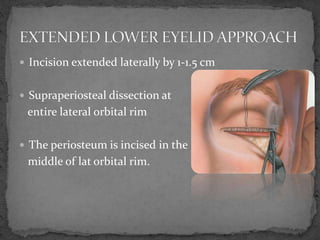
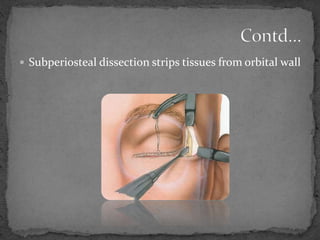
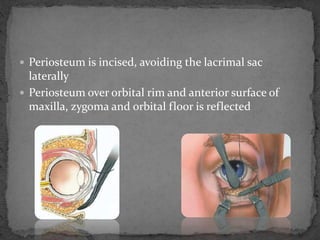
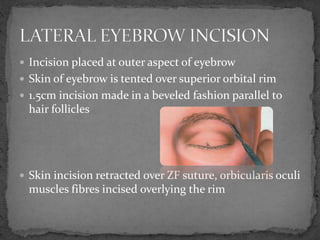
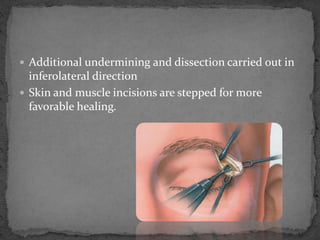
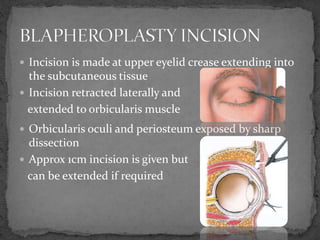
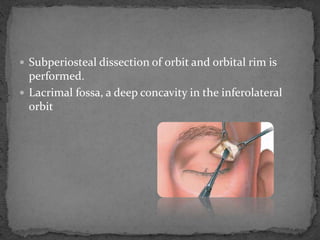
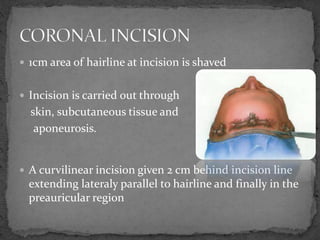
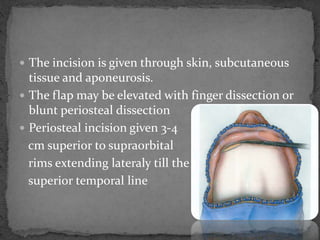
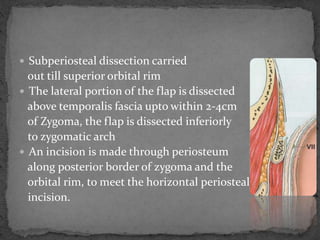
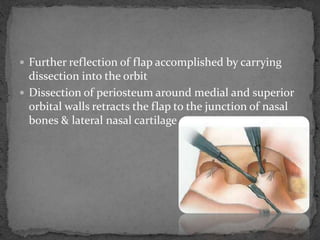
This document describes various surgical approaches for accessing the orbital rim and floor. It outlines several incision types including transcutaneous, subciliary, subtarsal, infraorbital, and lateral eyebrow incisions. For each incision, it provides details on placement, depth, and the steps of dissection and tissue retraction to access the periosteum and allow for subperiosteal dissection of the orbital wall. Key approaches discussed are the lateral eyebrow incision, upper blepharoplasty incision, coronal incision, and lateral canthotomy incision.