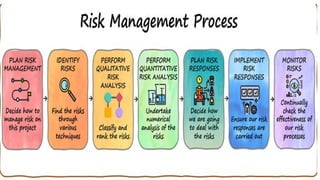
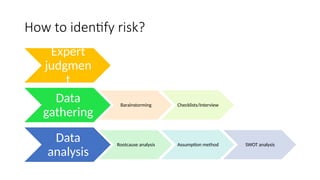
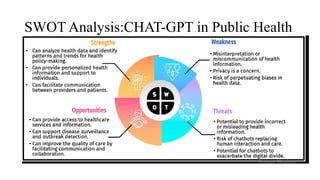
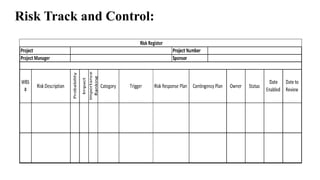
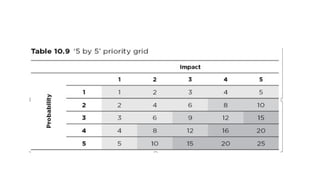
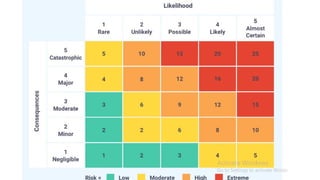
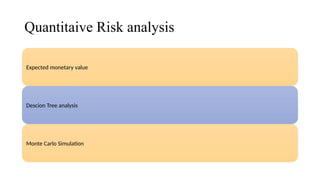
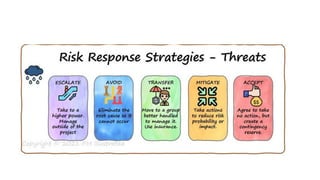
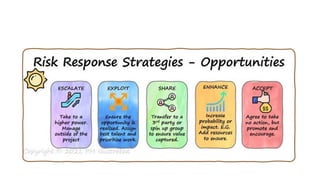
The document outlines the principles and processes of risk management in project management according to the PMBOK® Guide, emphasizing continuous evaluation of risks to optimize project outcomes. It describes various methods for identifying risks, including expert judgment and SWOT analysis, and details the processes for qualitative and quantitative risk analysis, including expected monetary value and decision tree analysis. The document also highlights the importance of ongoing risk monitoring, response planning, and the necessity to manage contingency reserves to address identified and emerging risks.