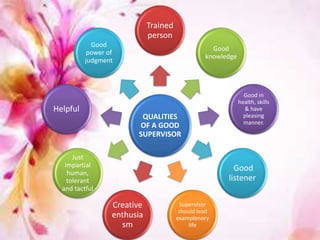
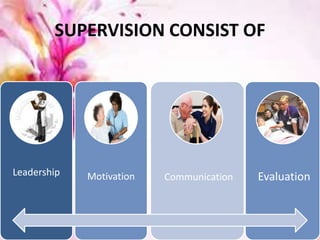
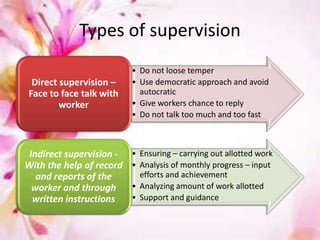
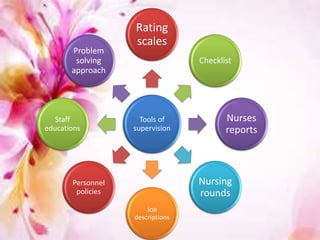
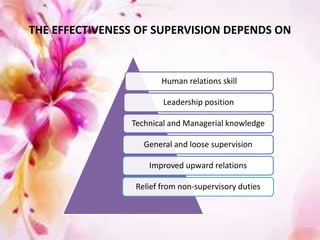
This document discusses supervision in nursing. It defines supervision and lists its objectives as helping subordinates work skillfully, developing their capacity, promoting teamwork, and bridging personal and organizational goals. The principles of supervision include aiming for growth, improving thinking, formulating objectives, and stimulating interest. A supervisor is responsible for quality, production, equipment, employees, training, and morale. Qualities of a good supervisor include being trained, knowledgeable, healthy, and having good listening, leadership, creativity, judgment, and human skills. The effectiveness of supervision depends on human relations skills, leadership, technical/managerial knowledge, and improved upward relations. Problems can include personnel shortages, individual differences, outdated policies, and ill health.