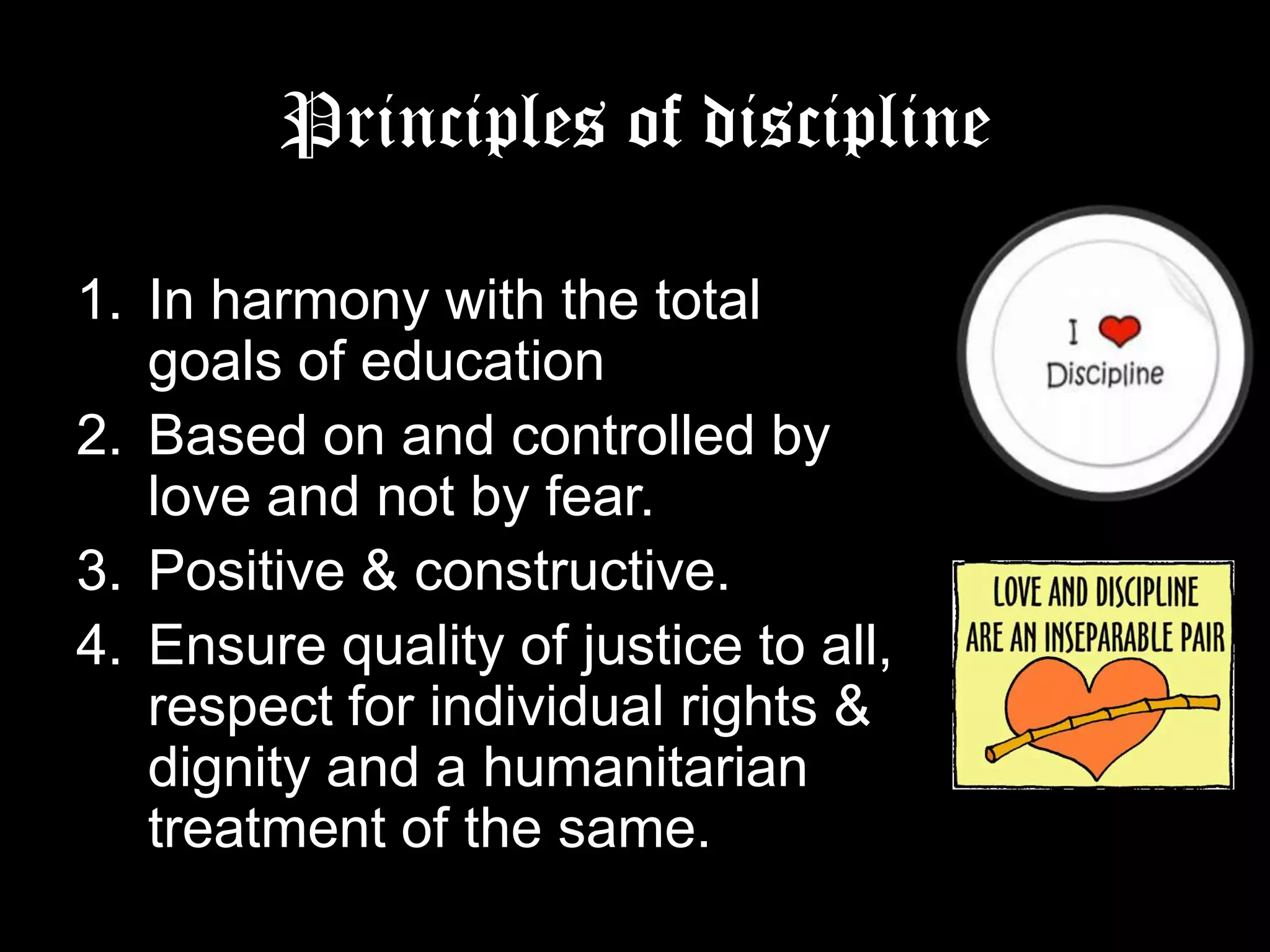
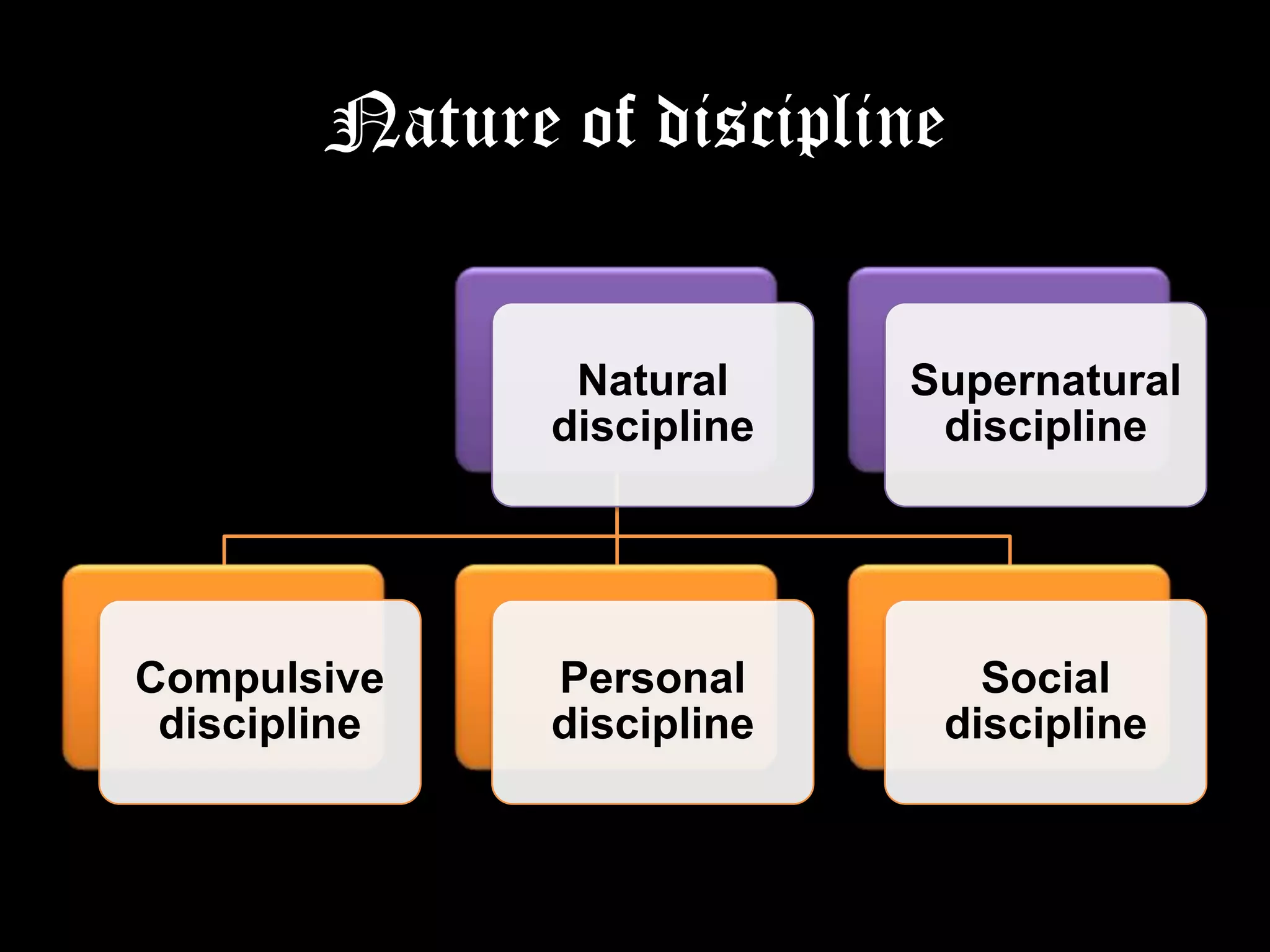
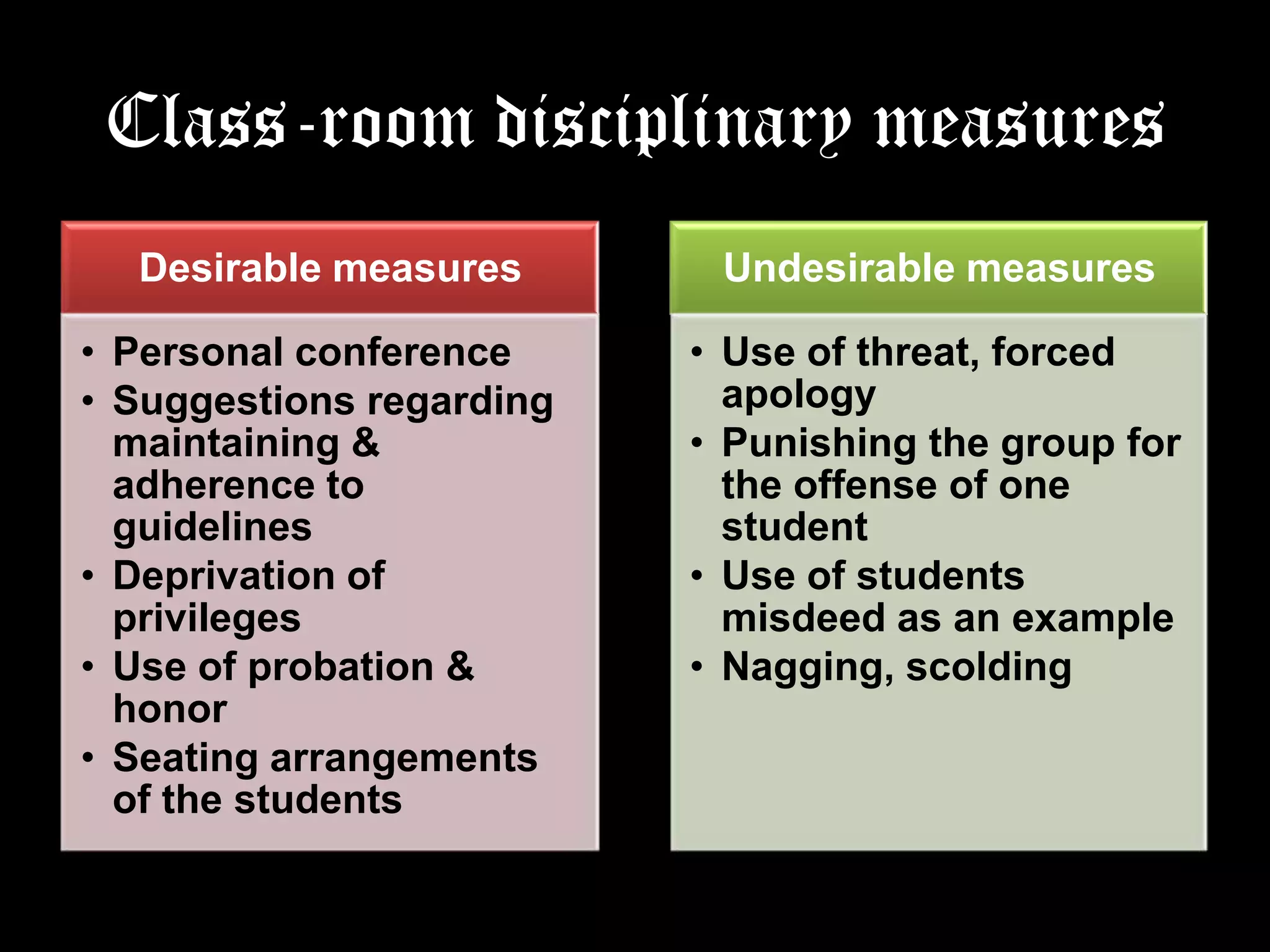
Discipline is defined as the training and development of students through instruction and exercises to regulate behavior and bring order and efficiency. The document outlines several principles of discipline including that it should be in harmony with educational goals, based on love rather than fear, preventative and corrective, and never retributive. Different types of discipline are discussed such as authoritarian, democratic, self-discipline, and assertive discipline. Classroom disciplinary measures and maintaining discipline are also explained. The conclusion emphasizes that discipline is vital for education by controlling behavior to achieve objectives and guidelines help create a student-centered environment.