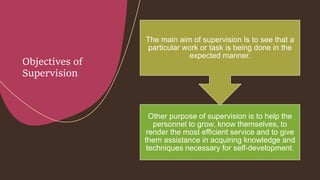
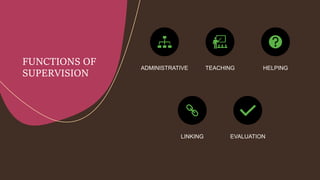
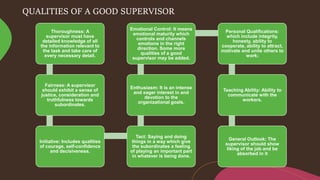
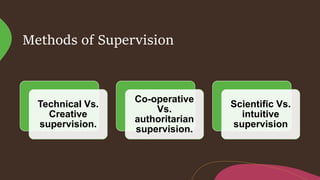
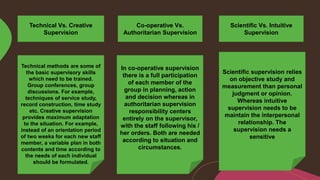
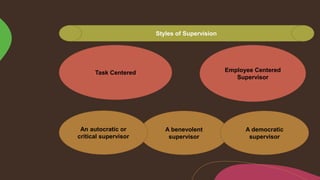
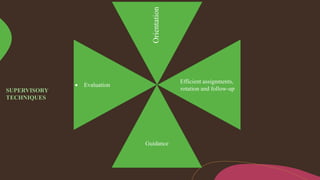
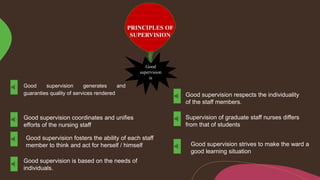
Supervision involves overseeing the work of others and ensuring it is performed appropriately. The main goals of supervision are to deliver high quality healthcare services, help staff reach their highest potential, and evaluate performance to improve outcomes. A good supervisor exhibits qualities like thoroughness, fairness, initiative, tact, and emotional control. Effective supervision utilizes various techniques such as direct observation, group discussions, orientation, and evaluation to guide, teach, and support staff. Principles of good supervision include respecting individuals, fostering independent thinking, creating a supportive learning environment, and stimulating continuous self-improvement.