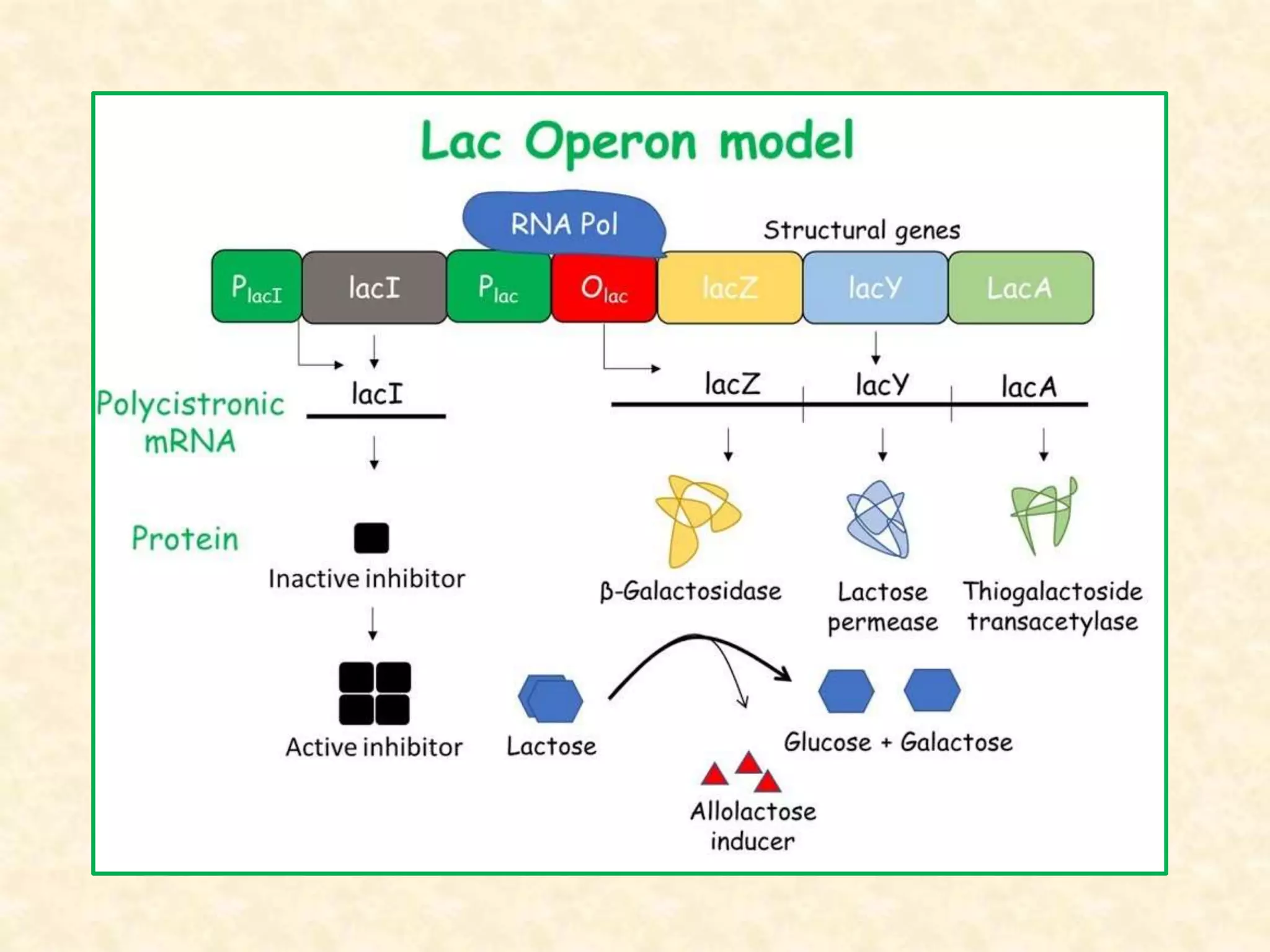
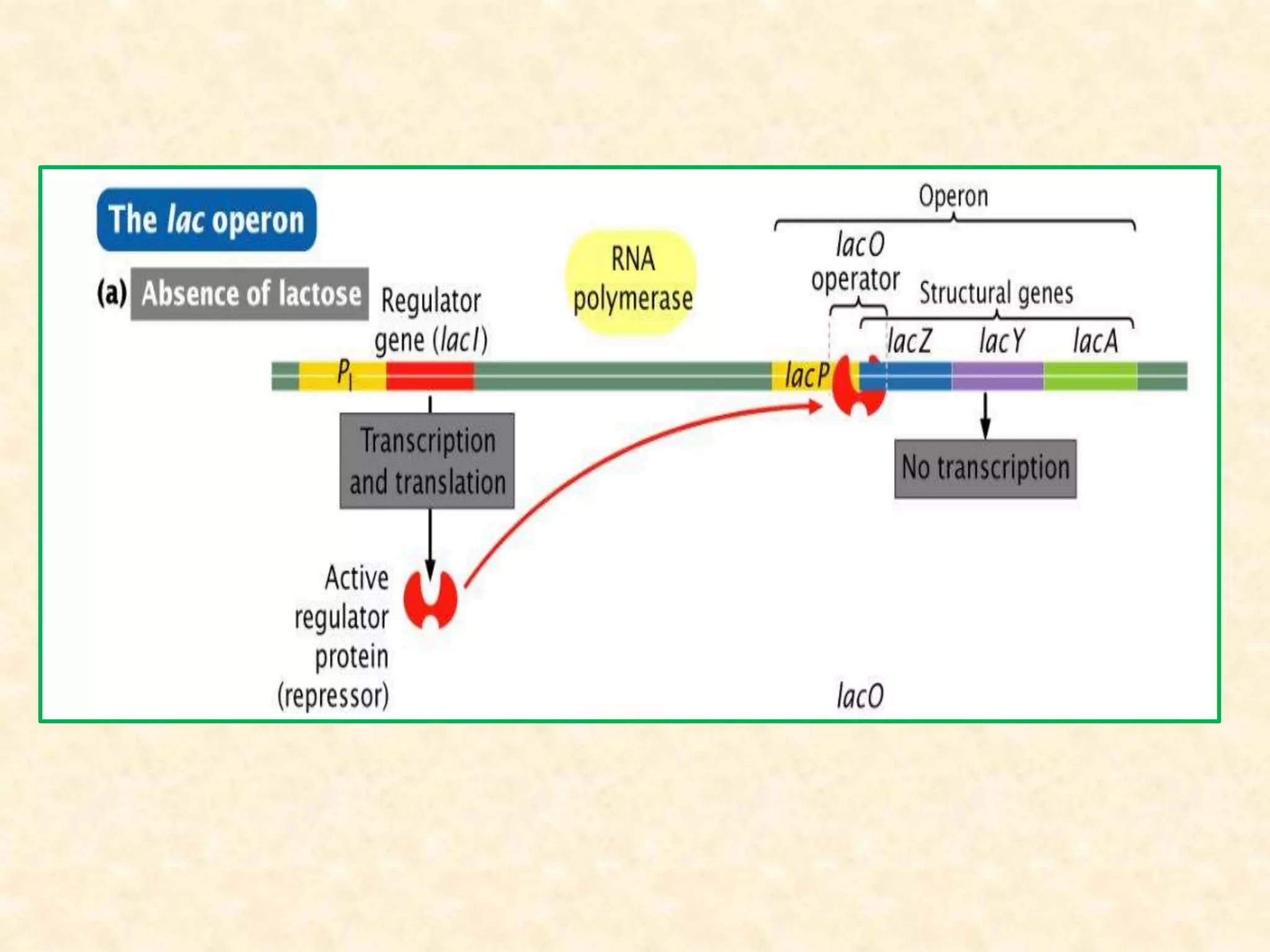
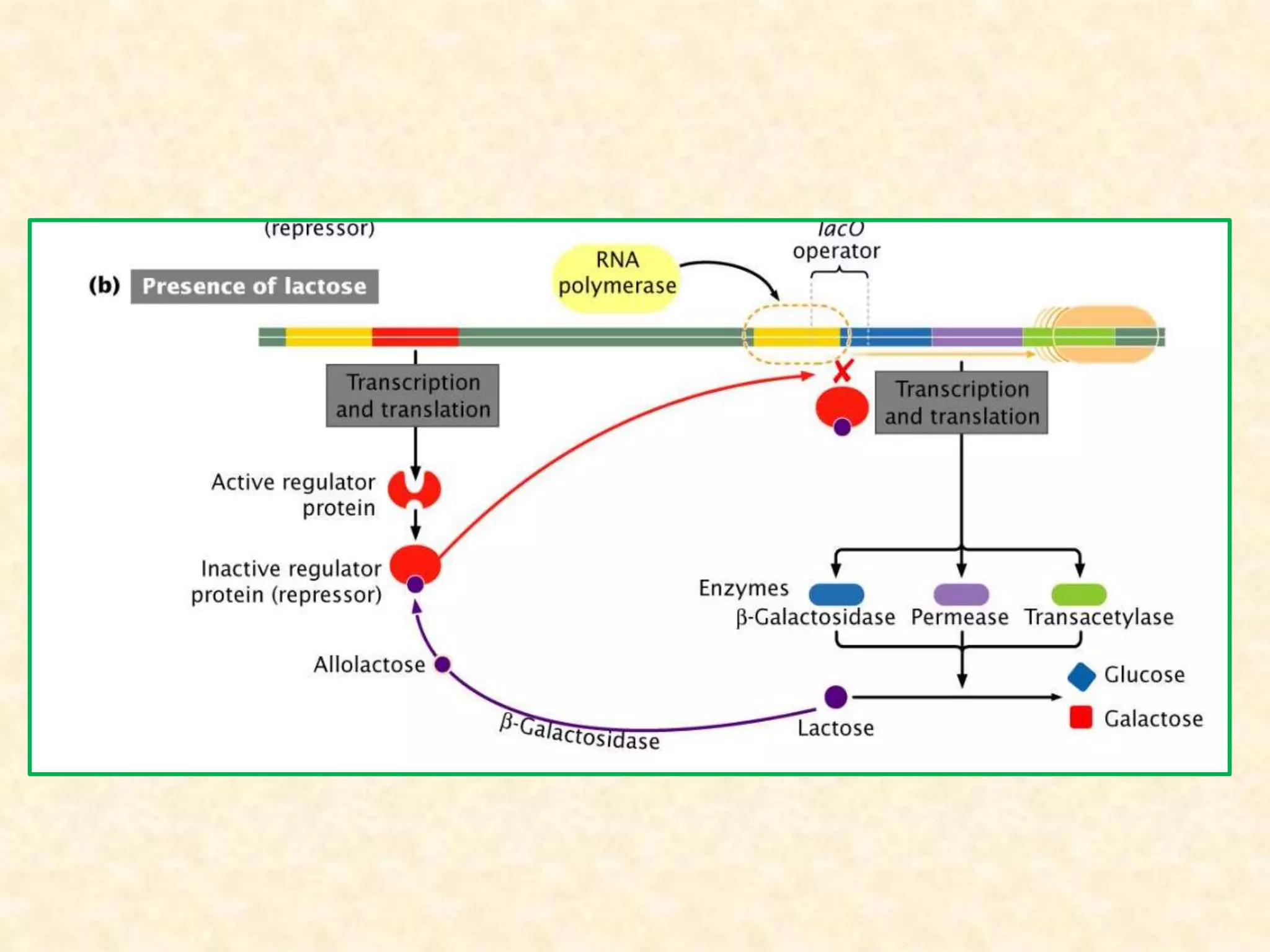
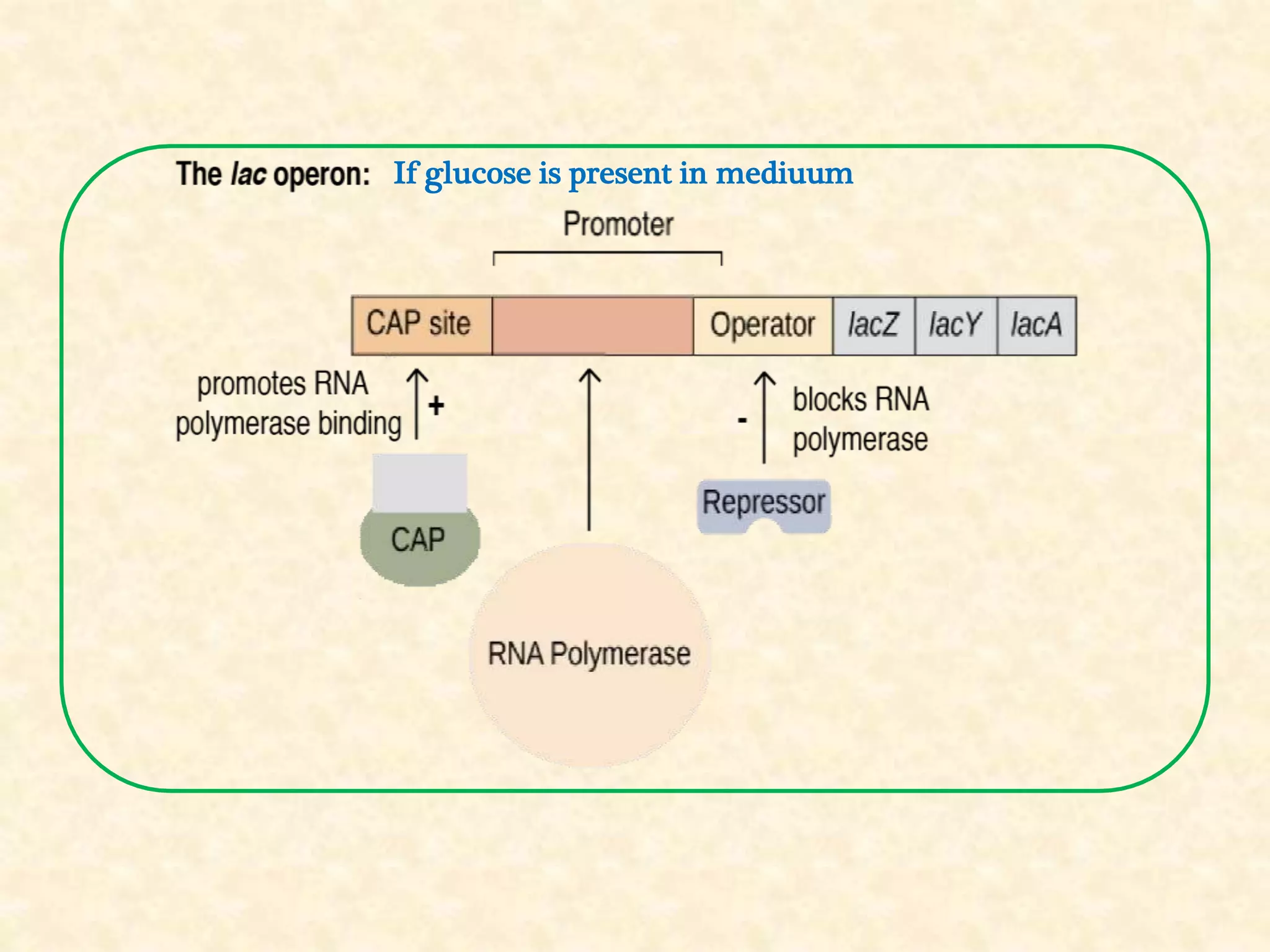
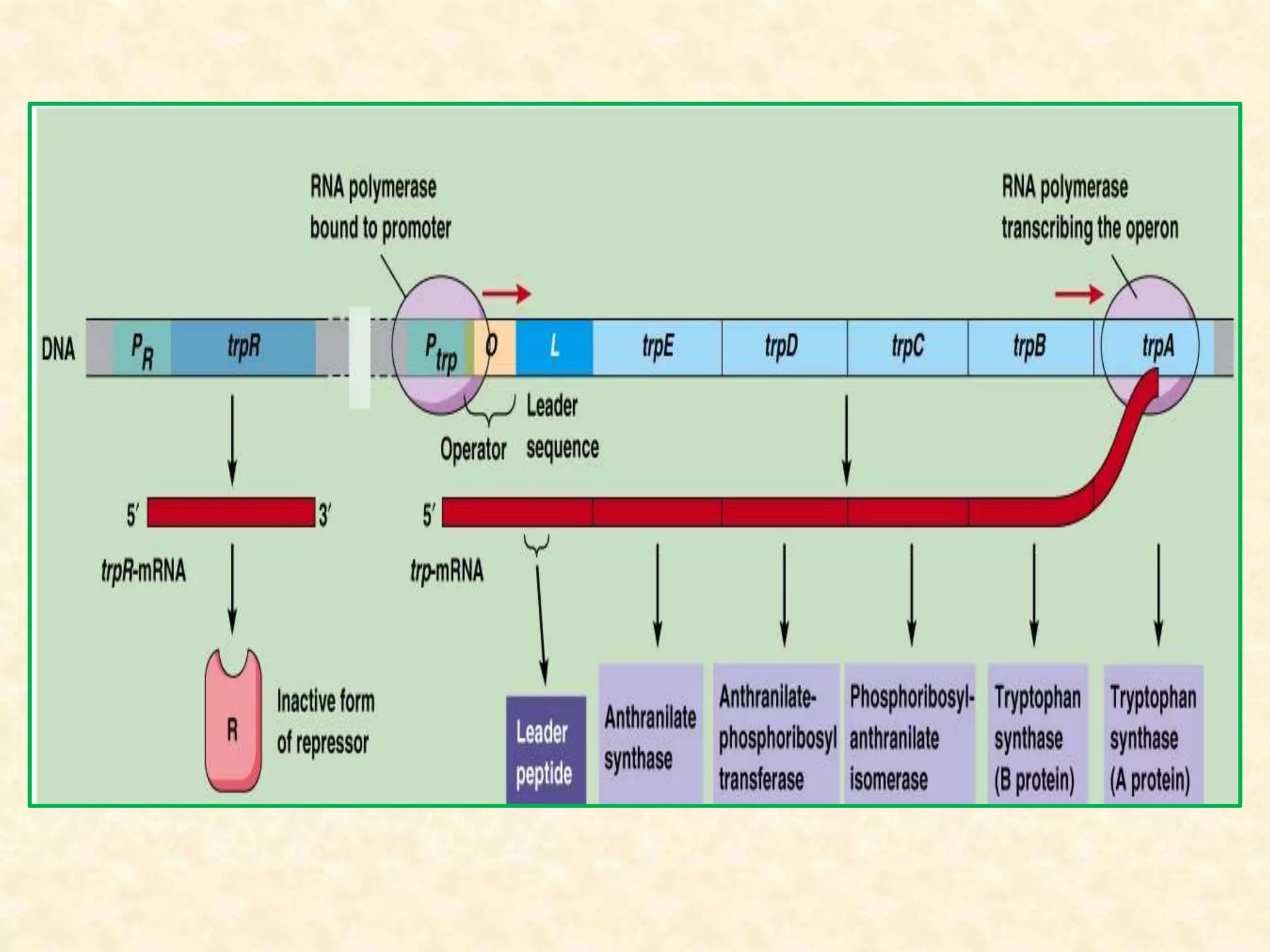
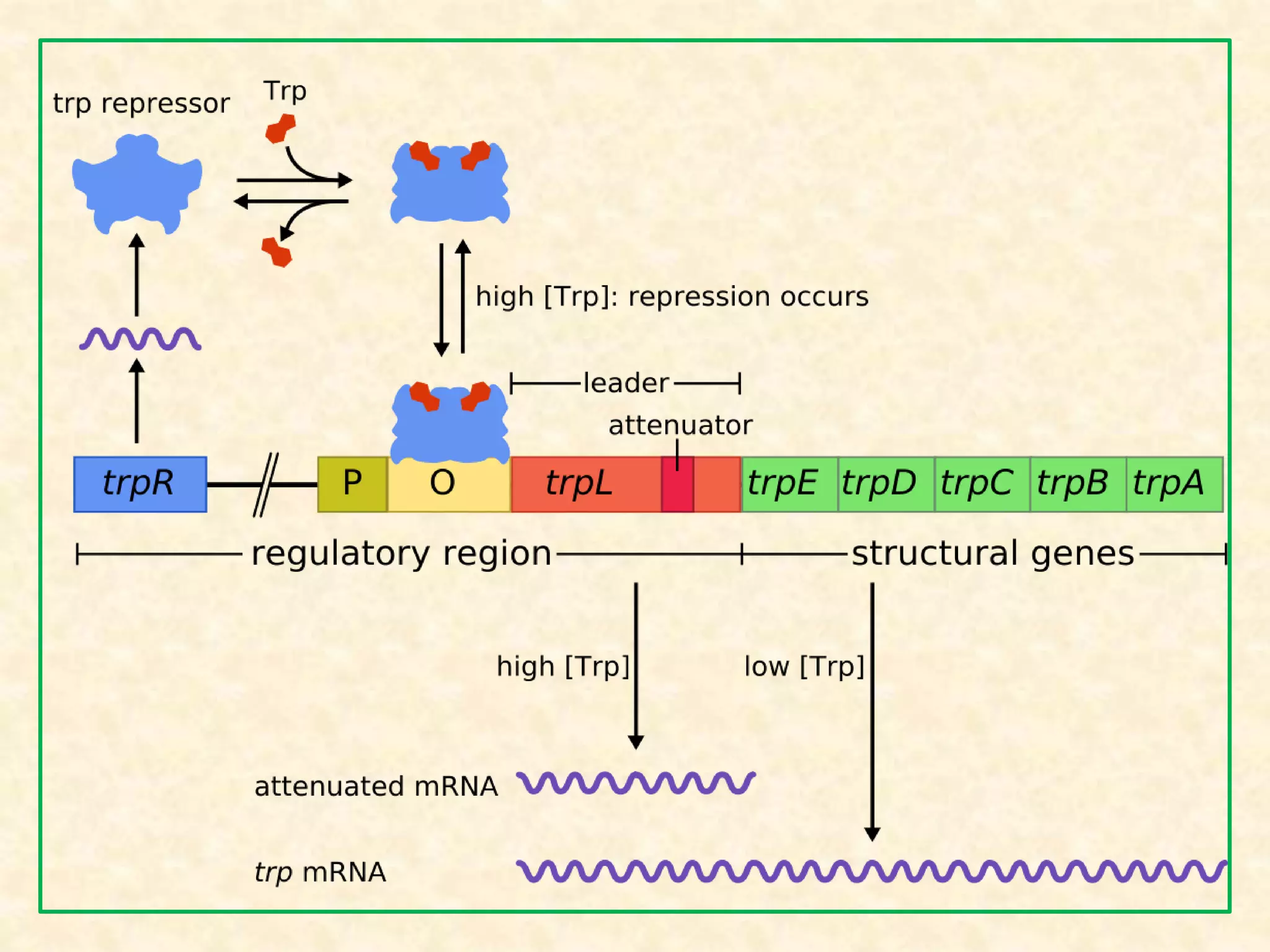
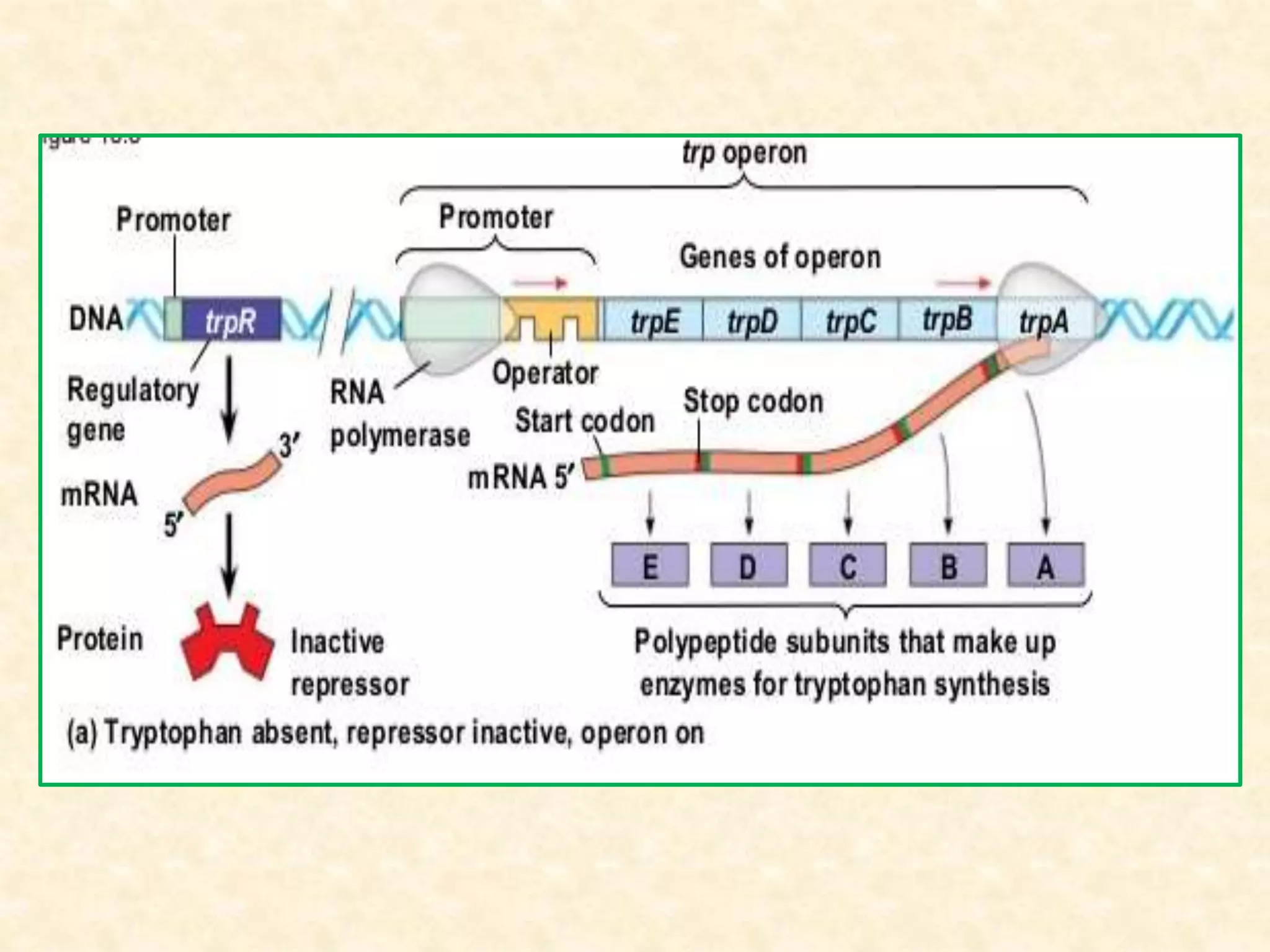
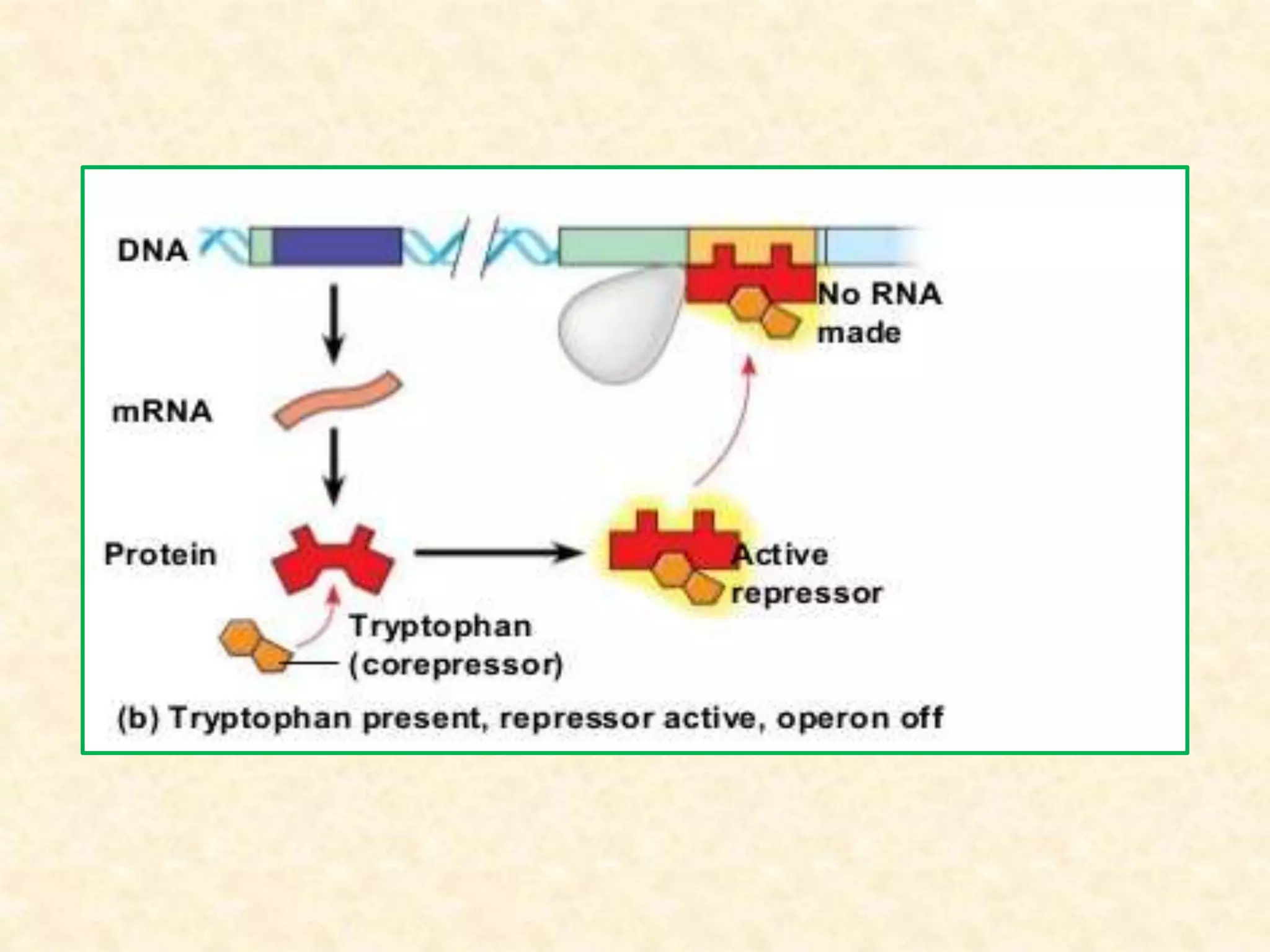
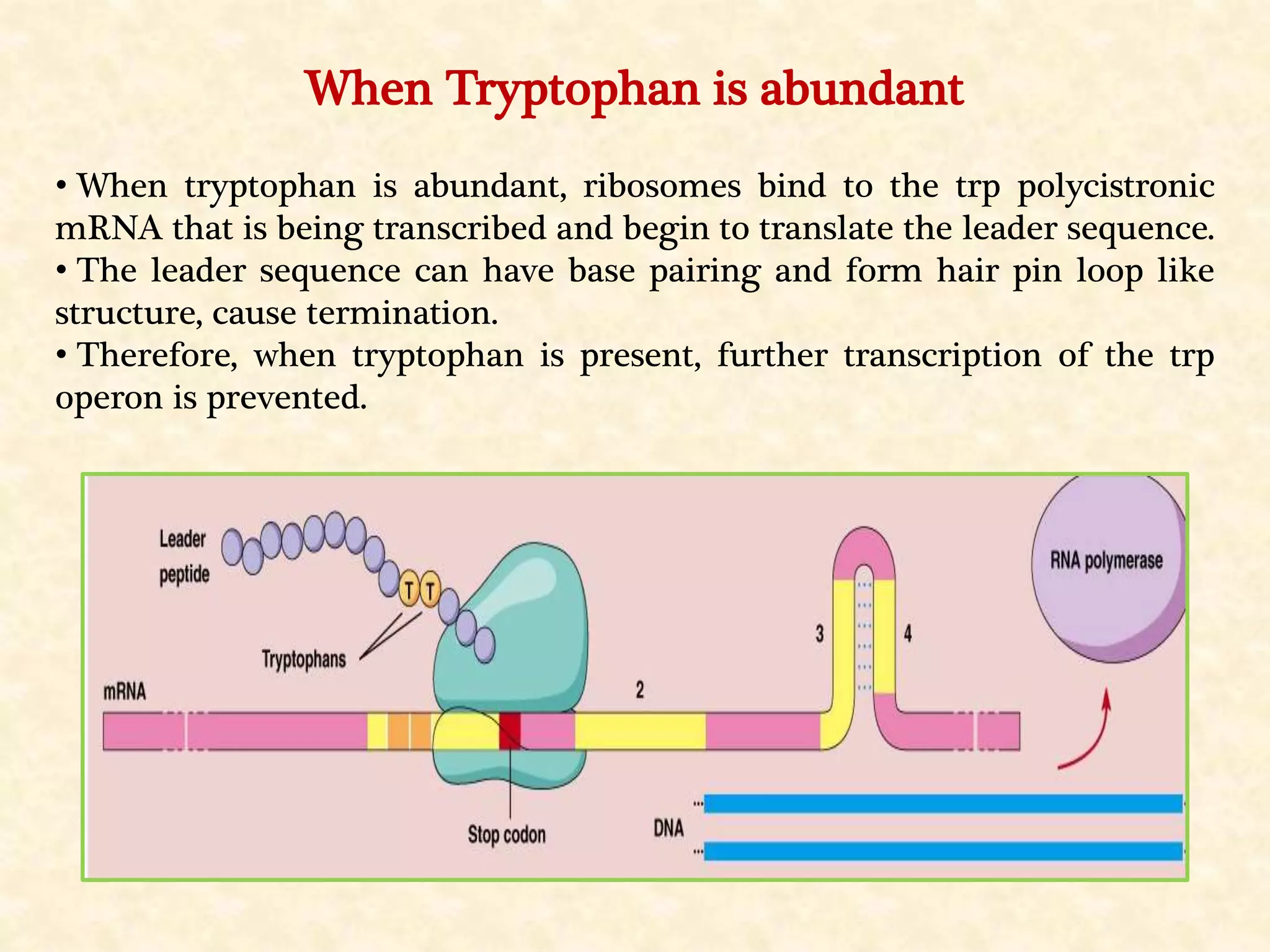
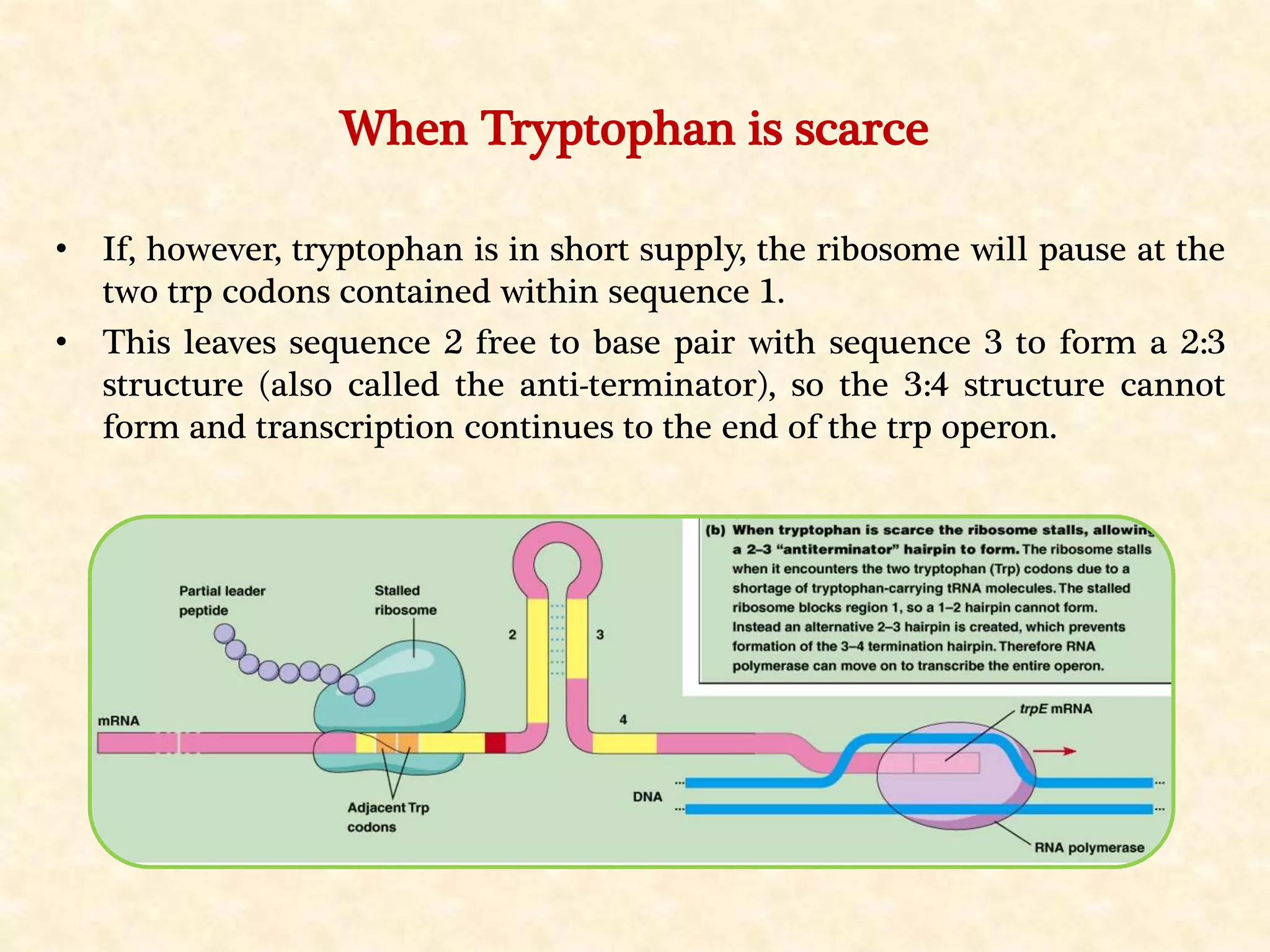
The document summarizes gene expression in prokaryotes. It discusses how prokaryotic genes are organized into operons that are regulated coordinately. It provides examples of the lac and trp operons. The lac operon encodes enzymes for lactose metabolism and is induced by lactose. The trp operon encodes enzymes for tryptophan synthesis and is repressed by tryptophan through binding of the trp repressor to the operator. Both operons utilize repressors and operators to control transcription in response to substrates or end products.