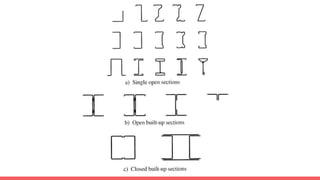
The document discusses structural steel used in construction. It describes the different types of steel based on carbon content and their properties. It also discusses reinforcement steel and structural steel sections used in construction. The main types of reinforcement steel discussed are mild steel, medium tensile steel, and high yield strength deformed bars. The main types of structural steel sections described include rolled sections like angles, channels, I-sections, tubes, plates, as well as built-up sections. Light gauge steel sections made from thin steel sheets are also summarized.