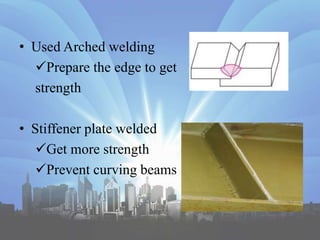
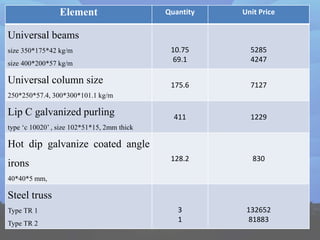
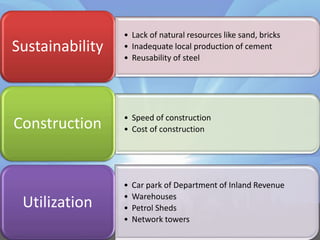
This document discusses steel building construction. It outlines the advantages like strength, light weight, and speed of construction. The main disadvantages are the higher cost and need for fire protection. Steel buildings are commonly used for storage, skyscrapers, offices, and temporary structures. The document provides details on site investigation, fabrication, key elements like beams and columns, and cost estimates. It concludes that steel building construction is suitable for Sri Lanka due to the lack of natural resources, reusability of steel, and speed of construction.