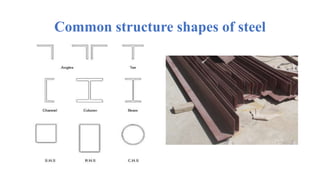
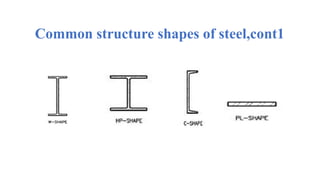
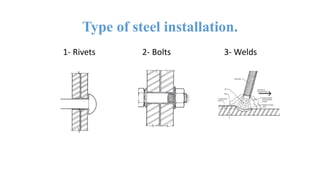
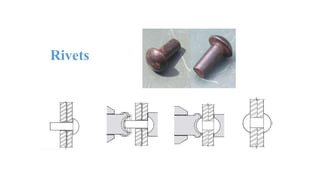
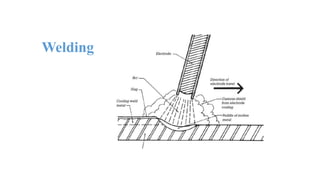
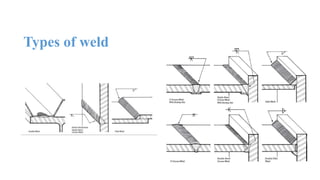
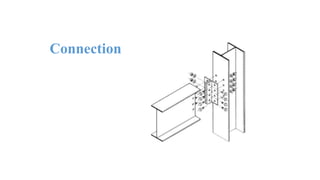
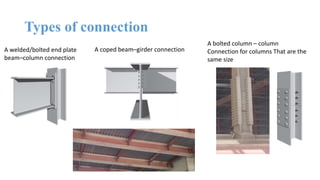
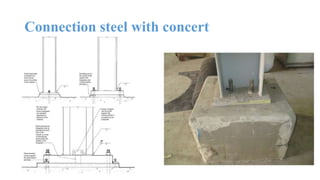
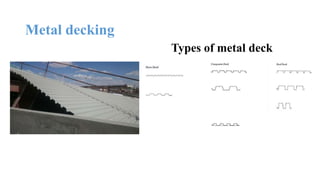
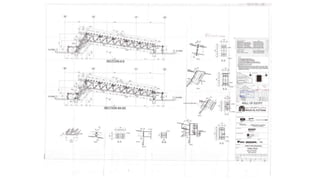
The document discusses the construction of a steel structure for the Canadian International College, detailing the advantages and disadvantages of steel, manufacturing processes, and structural steel standards in the US and Europe. It includes information on different shapes of steel, thermal properties, fire resistance, and installation methods. The presentation is collaboratively authored by students and presented to faculty members.