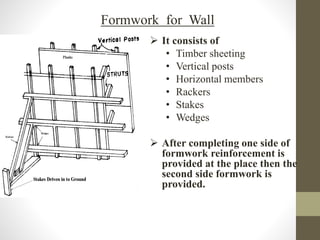
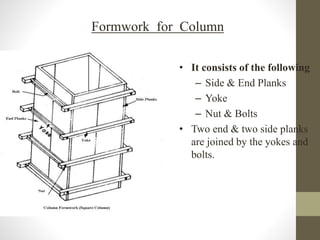
The document discusses advance construction equipment with a focus on formwork, outlining its purposes, materials (such as steel and timber), and essential qualities like safety, quality, and economy. It details the construction steps for various structural elements (walls, columns, slabs, stairs), the factors influencing formwork removal timing, maintenance needs, and cost implications, which can range from 30% to 60% of concrete costs. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of using steel formwork and the types of loads that need to be considered during construction.