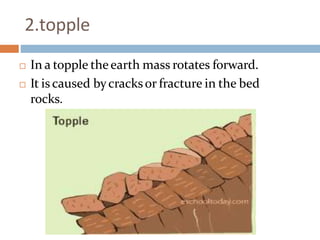
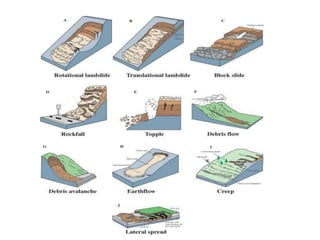
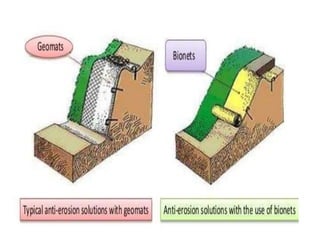
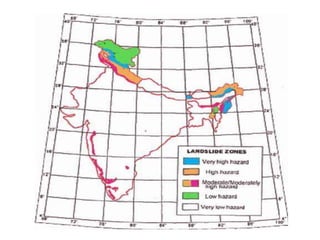
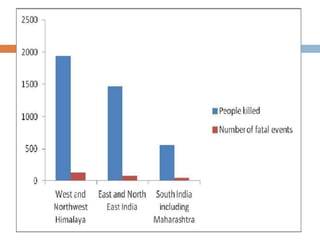
The document defines landslides as the sudden flow of rock, mud, and debris down the side of a slope. Landslides are natural hazards caused by factors like earthquakes, heavy rainfall, temperature changes, deforestation, mining, and steep slopes. There are different types of landslides classified by their movement and materials, including slides, topples, falls, and flows like debris flows and mudflows. Landslides can be deadly and cause damage by blocking roads, rivers, and damaging buildings and vegetation. Areas at high risk of landslides in India include the Himalayan region, Northeast states, and Western Ghats.