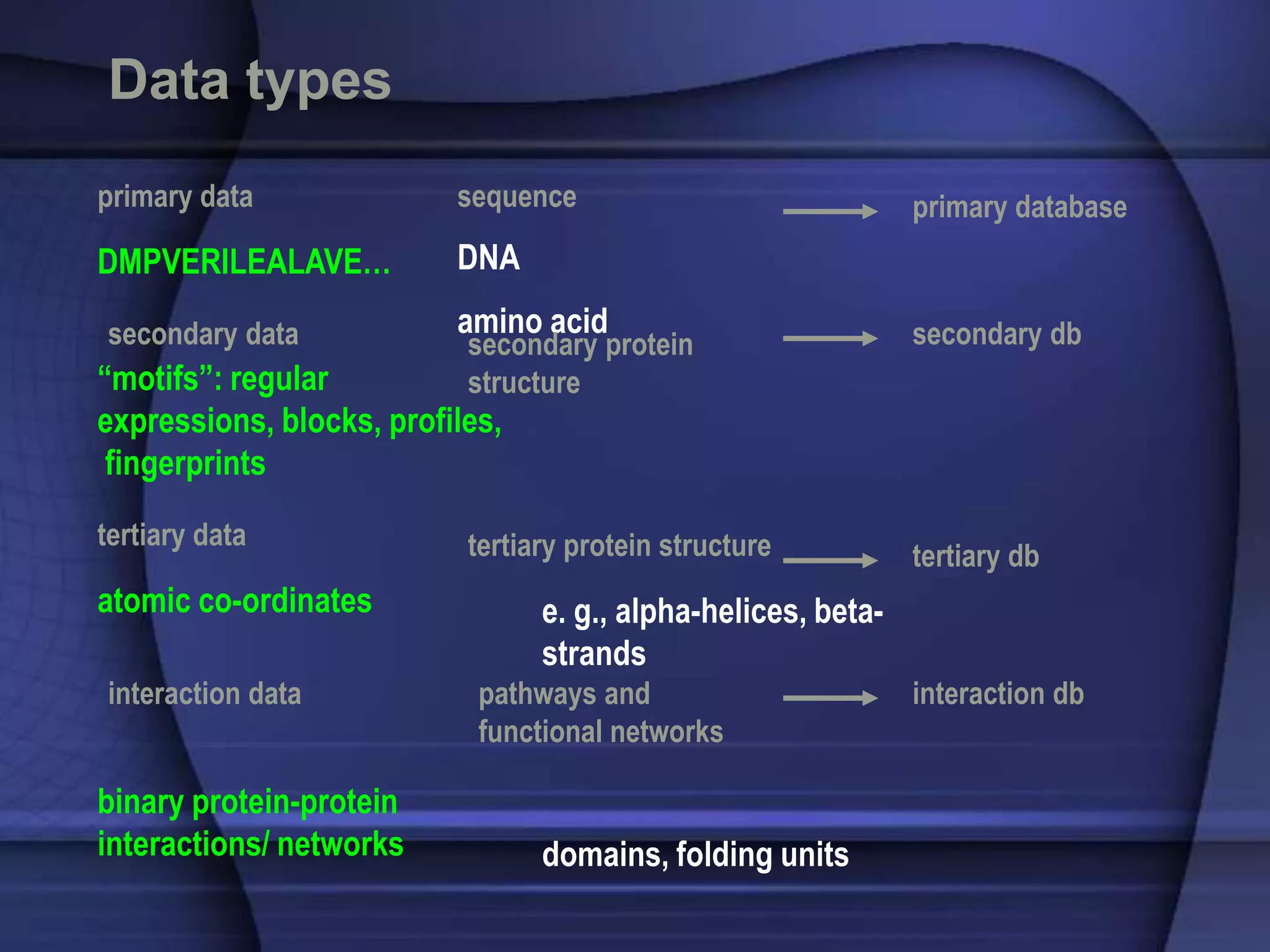
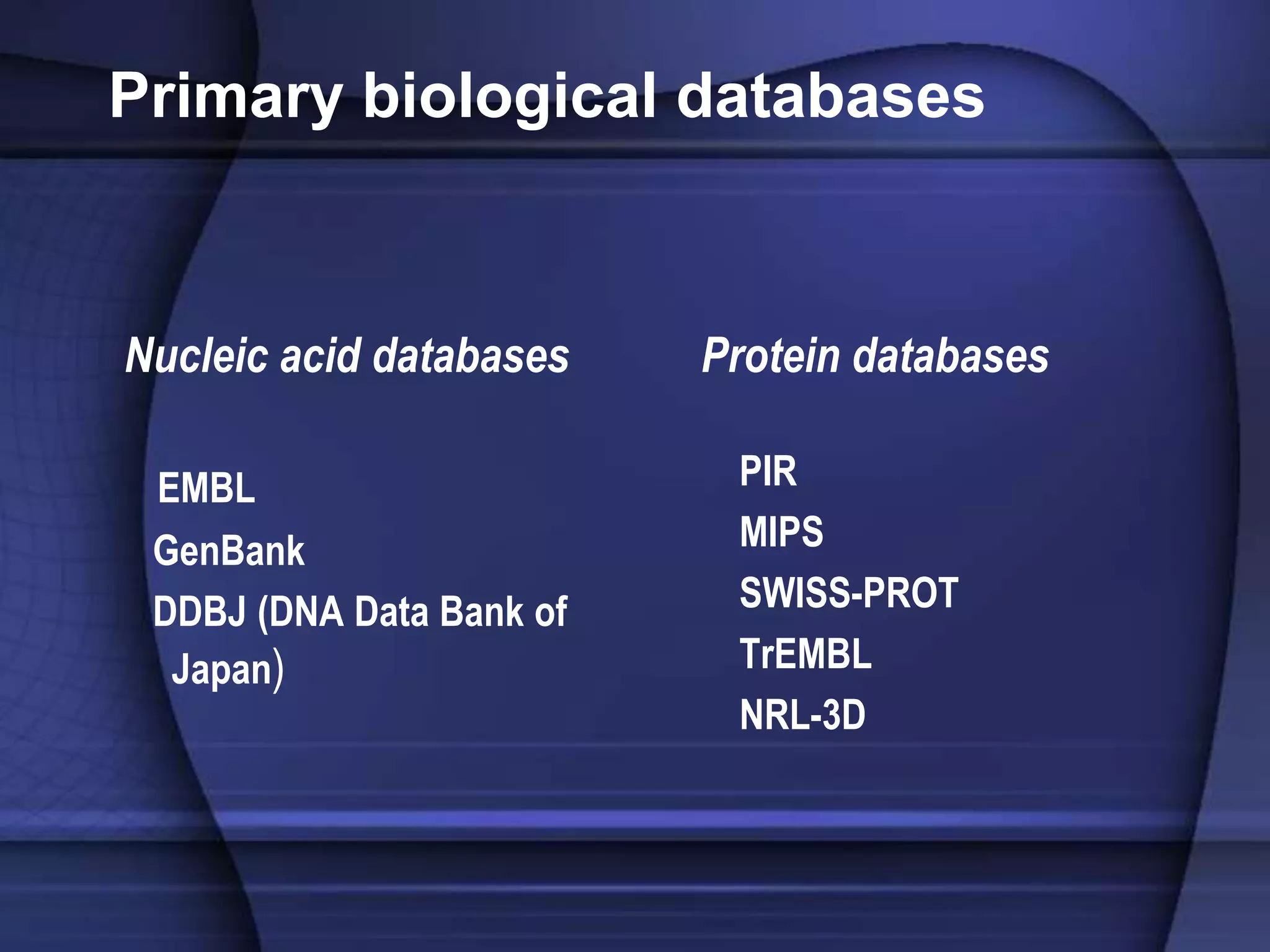
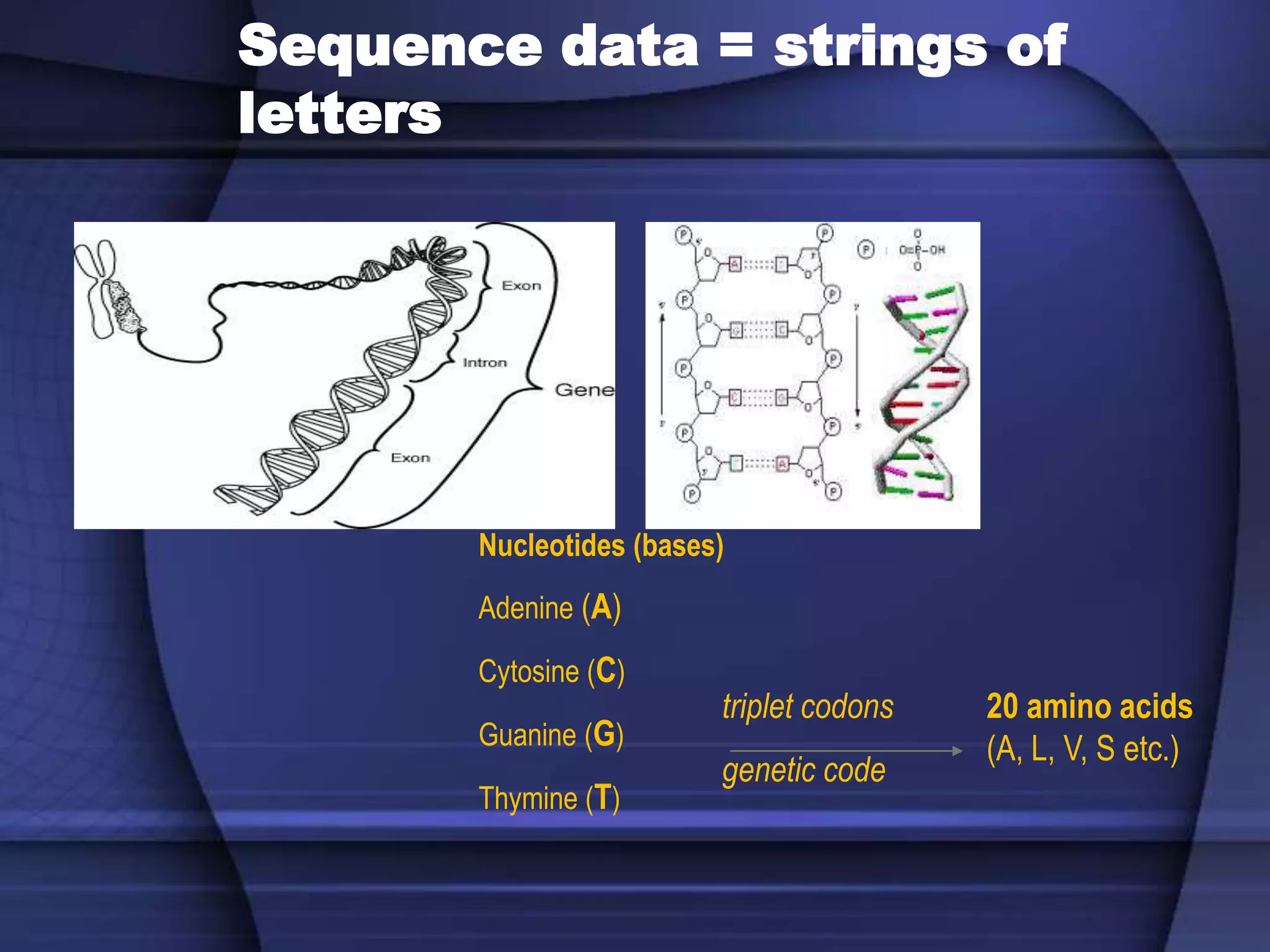
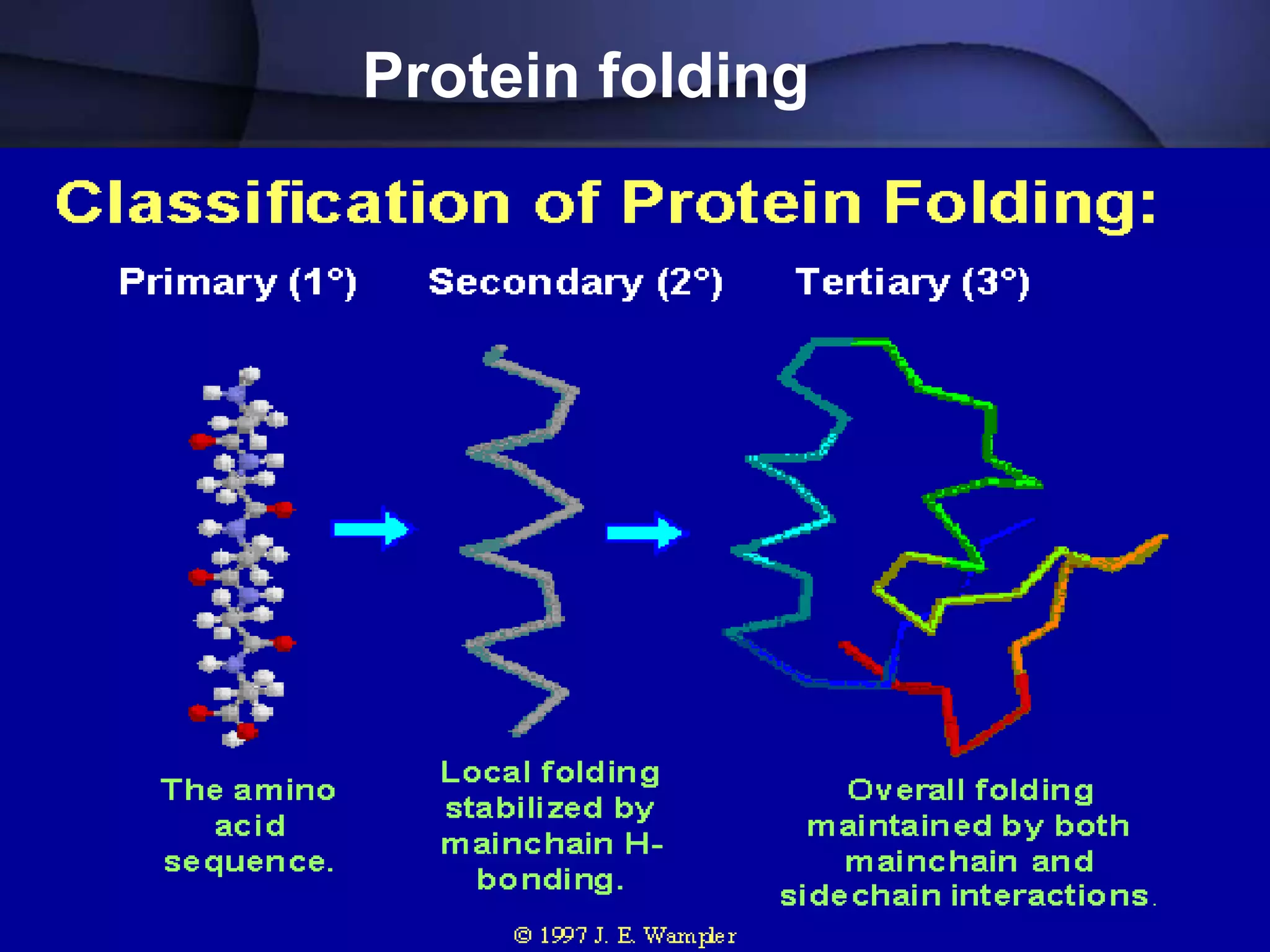
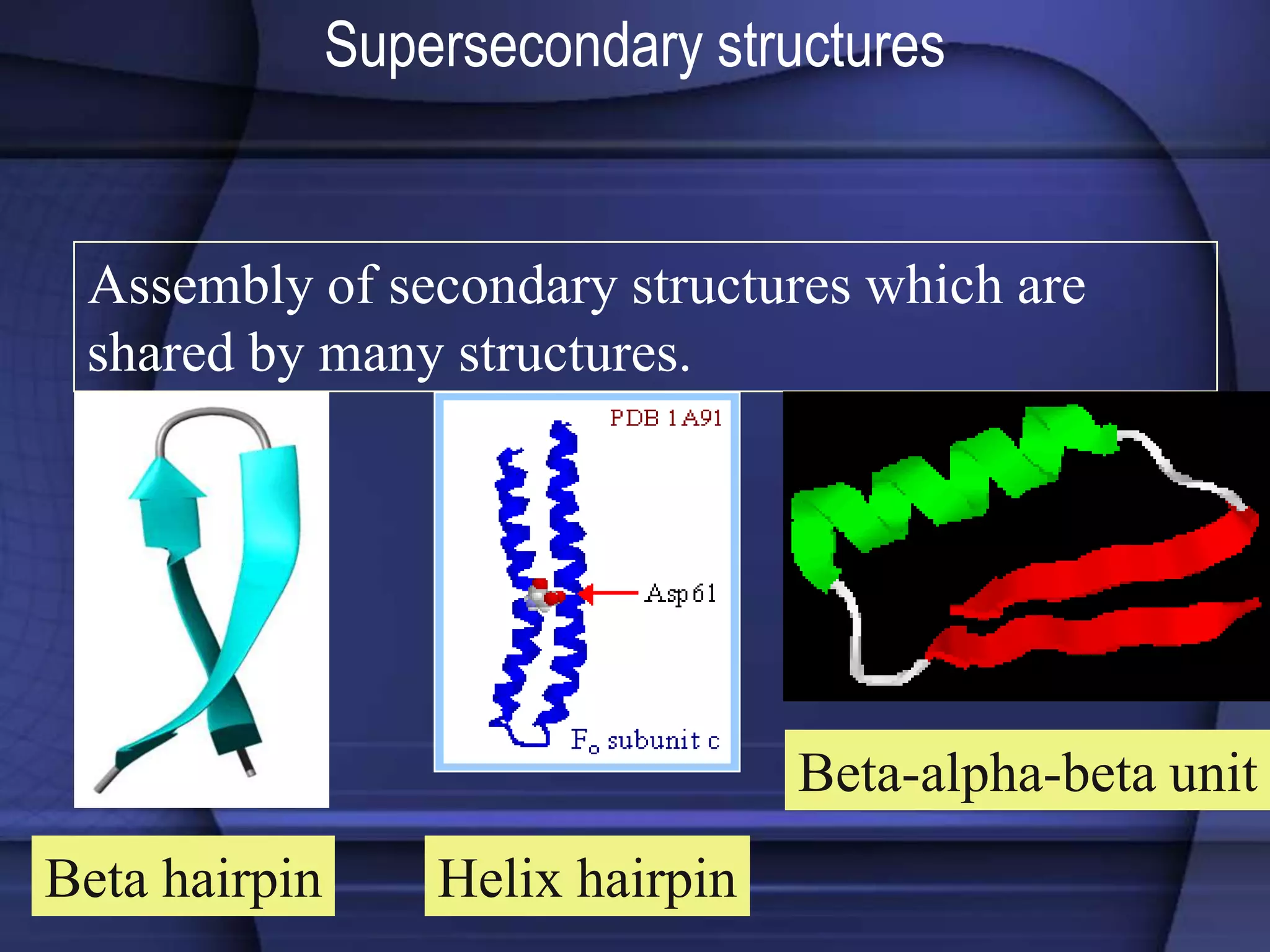
The document discusses various types of biological databases that contain information on amino acids, nucleic acids, proteins and their structures. It describes primary databases that contain sequence data as well as secondary and tertiary databases that include protein structure information like motifs, domains and atomic coordinates derived from techniques like X-ray crystallography. Major databases discussed include Swiss-Prot, PDB, EMBL and their roles in archiving sequence data, annotating proteins and classifying structural information using systems like SCOP and CATH.