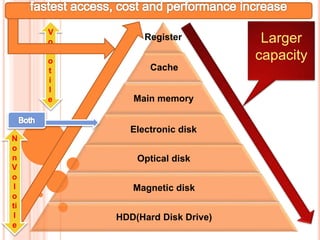
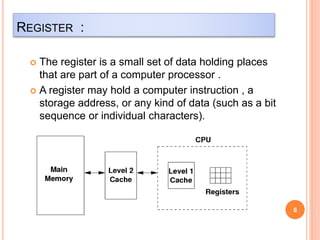
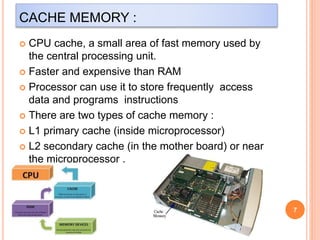
This document discusses different types of computer memory structures. It introduces registers and cache memory as the fastest types of volatile memory closest to the CPU. Registers are very small memory locations inside the CPU used to store instructions and data during processing. Cache memory is faster than main memory and stores frequently used data and instructions from main memory. Volatile memory loses its data when power is removed, while non-volatile memory retains data permanently in storage devices like hard drives, USB drives, and optical discs.