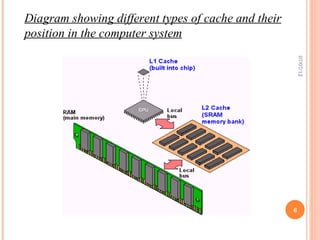
Cache is a small amount of fast memory located close to the CPU that stores frequently accessed instructions and data. It speeds up processing by allowing the CPU to access needed information more quickly than from main memory. Caches exploit the principle of locality of reference, where programs tend to access the same data/instructions repeatedly over short periods. There are multiple cache levels, with L1 cache being fastest but smallest and L3 cache being largest but slower. Caching improves performance dramatically by fulfilling over 90% of memory requests from the small cache rather than requiring slower access to main memory.