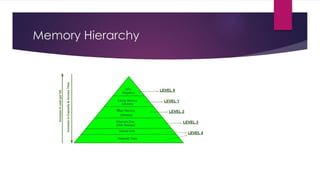
Computer memory can be temporary like RAM or permanent like ROM. RAM is used to store data and instructions temporarily and must be continually refreshed to retain its contents, while ROM can only read programs and data stored permanently. A computer uses a memory hierarchy with faster but smaller and more expensive memory like registers and cache close to the CPU, and larger but slower disk-based storage. This tiered approach allows the CPU to rapidly access critical data while leveraging inexpensive long-term storage.