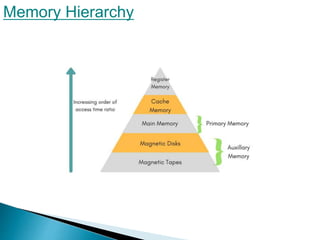
A memory unit contains storage devices that store binary information as bits. Memory can be classified as volatile, which loses data when power is off, or non-volatile, which retains data when unpowered. The total computer memory forms a hierarchy from slow auxiliary memory to faster main memory and cache memory. Main memory communicates directly with the CPU and auxiliary memory, and holds programs currently in use while transferring unused programs to auxiliary memory. Memory can be accessed randomly, sequentially, or directly depending on its type.