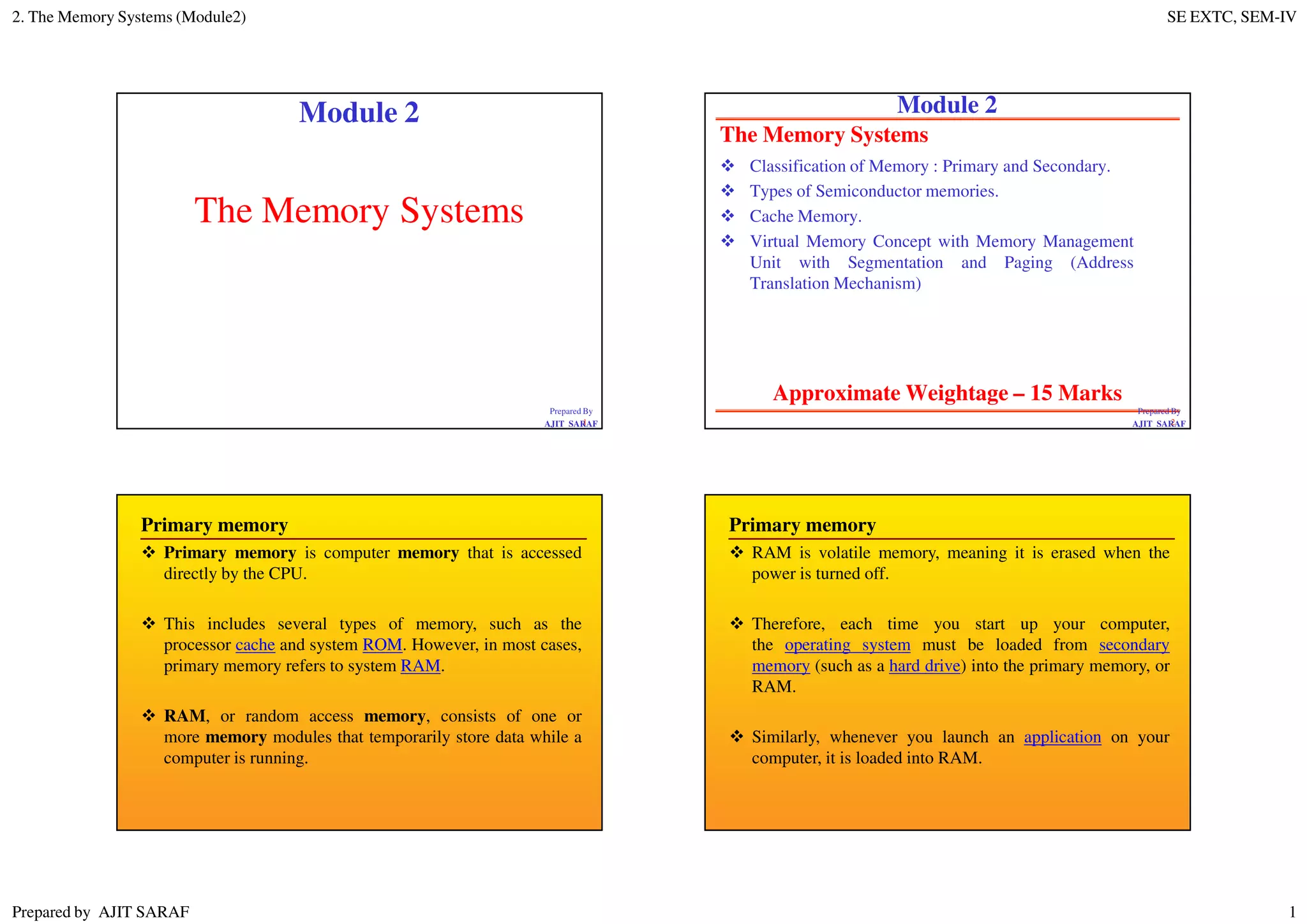
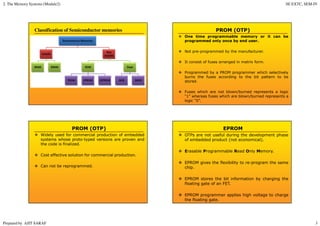
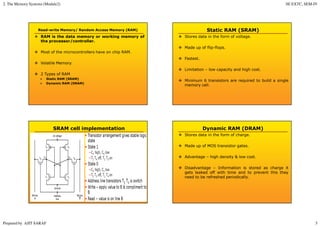
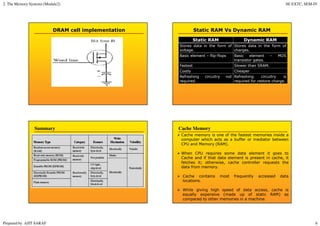
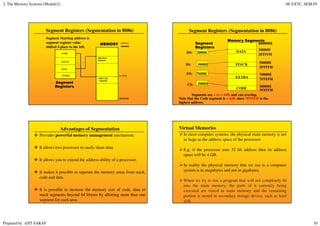
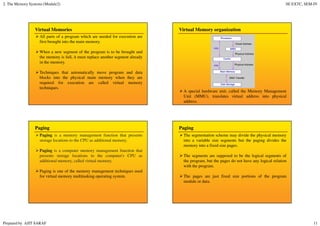
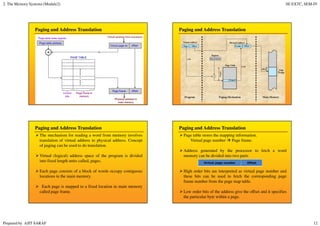
Primary memory (RAM) is directly accessed by the CPU and is much faster than secondary memory (hard drives, SSDs). The CPU loads programs and files from secondary memory into RAM in order to process them more quickly. RAM is volatile and loses its contents when powered off, while secondary memory is non-volatile. Cache memory acts as a buffer between the CPU and RAM to further improve access speed. Virtual memory allows programs to access more memory than is physically installed by paging memory pages to and from secondary storage.