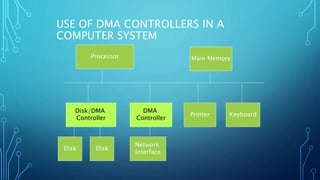
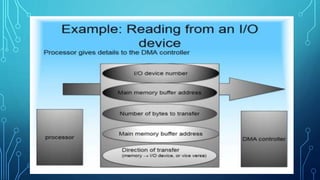
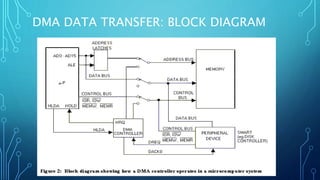
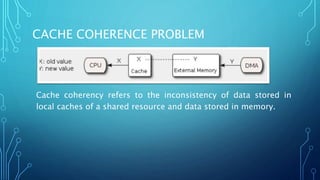
Direct memory access (DMA) allows certain hardware subsystems to access computer memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU). During DMA transfer, the CPU is idle while an I/O device reads from or writes directly to memory using a DMA controller. This improves data transfer speeds as the CPU does not need to manage each memory access and can perform other tasks. DMA is useful when CPU cannot keep up with data transfer speeds or needs to work while waiting for a slow I/O operation to complete.