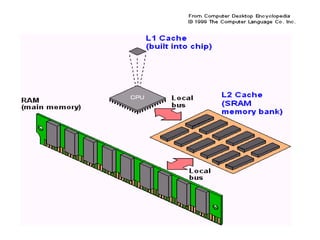
Cache memory is a small, fast storage used by the CPU to speed up data access by storing copies of frequently used memory locations. There are two primary types of cache memory: L1 (Level 1), which is integrated into the CPU, and L2 (Level 2), which is on a separate chip and feeds the L1 cache. L1 is smaller and faster than L2, making access to L1 quicker, while L3 can also exist as a larger cache level in some processors.