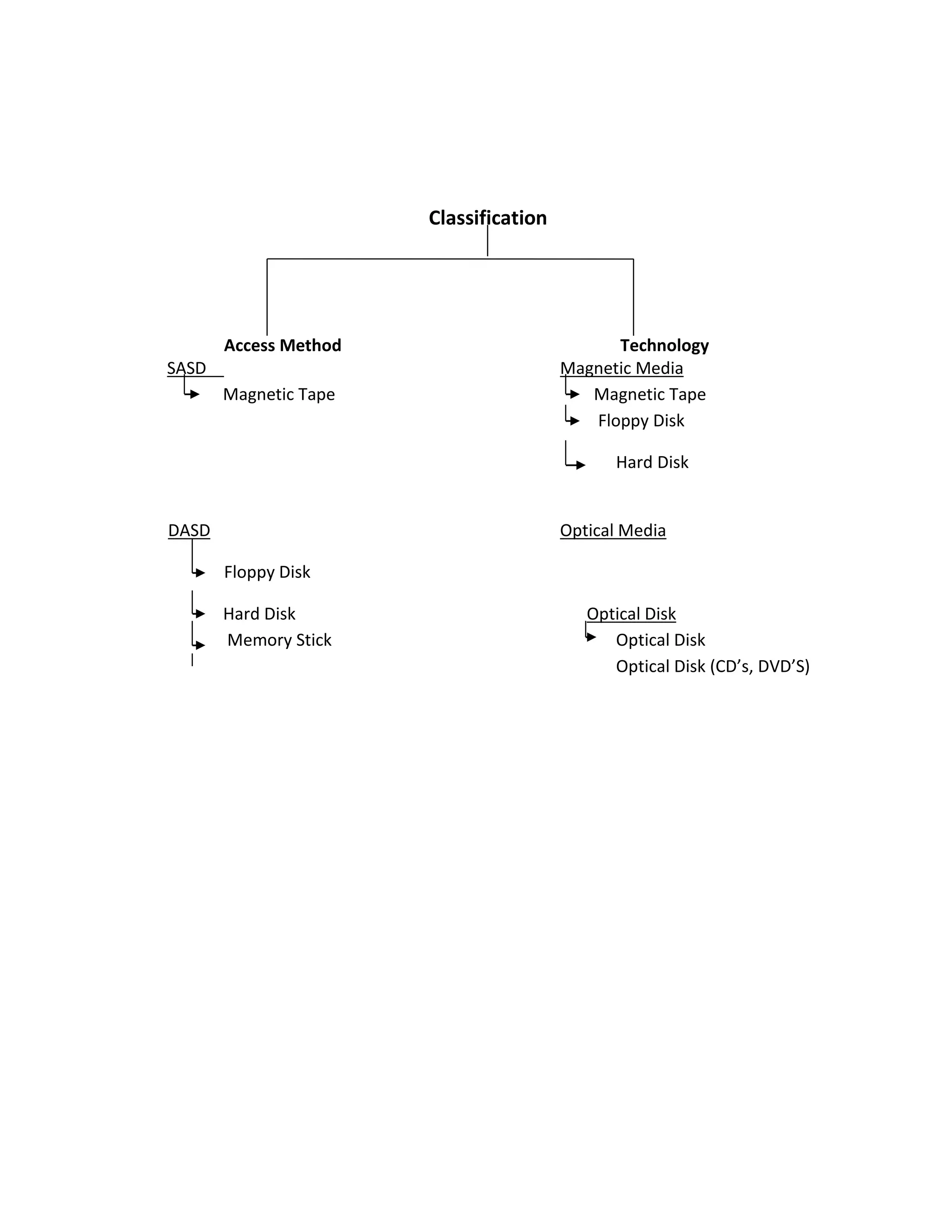
The document discusses and compares various types of secondary storage devices. It describes magnetic tape, floppy disks, hard disks, CD-ROMs, DVDs, and memory sticks. Magnetic tape provides archival storage but only allows sequential access. Floppy disks allow portability but have limited capacity. Hard disks have high storage capacity and access speeds but are not portable. Optical disks like CDs and DVDs can store large amounts of data reliably but have slower access times than hard drives.