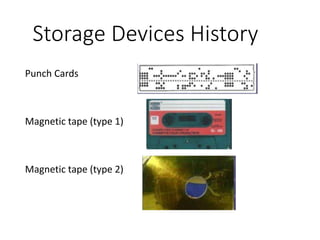
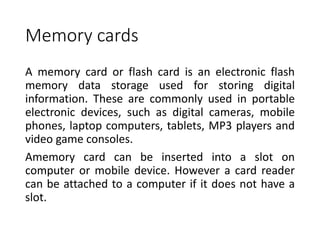
This document discusses various computer storage devices. It begins by defining basic units of storage like bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, etc. It then describes different types of primary storage devices like RAM and ROM as well as secondary storage devices like hard disks, CDs, DVDs, flash memory, and magnetic tapes. Specific storage devices are then discussed in more detail including hard disks, optical discs, magnetic disks, disk caches, and various memory cards. The document concludes by covering other older storage technologies like zip disks and super disks.