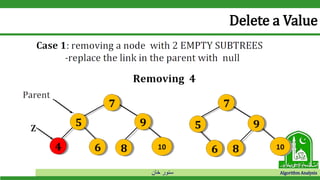
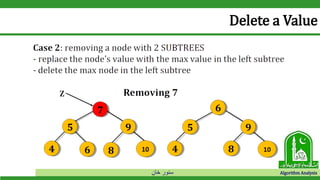
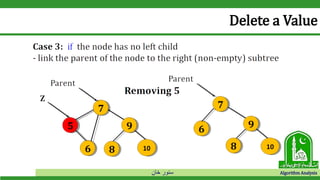
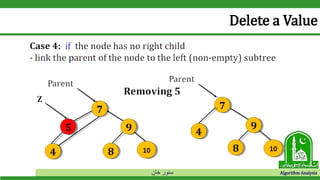
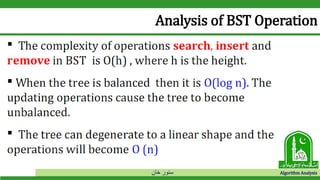
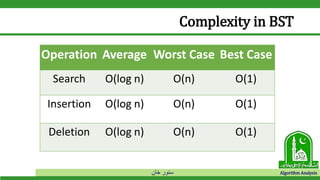
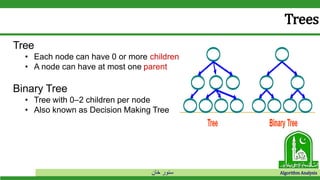
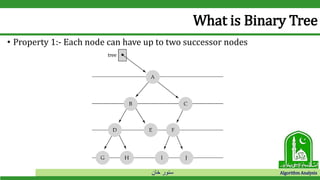
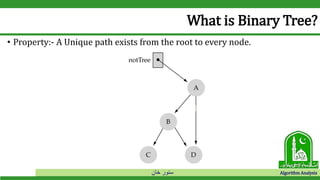
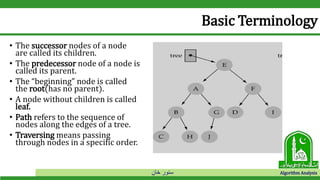
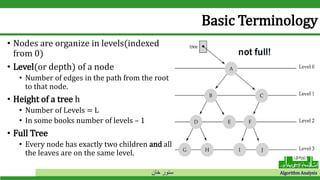
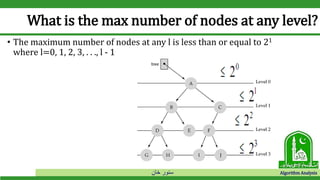
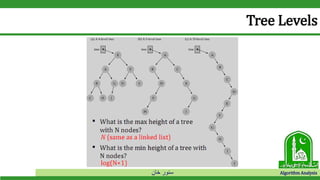
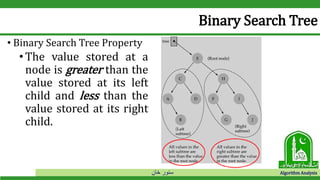
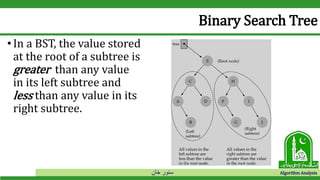
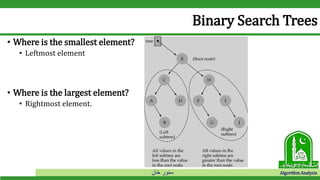
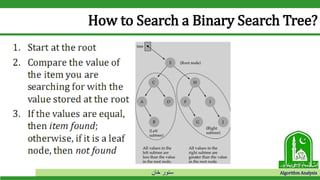
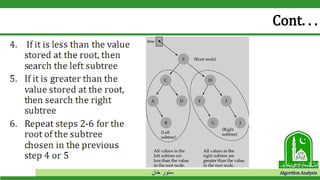
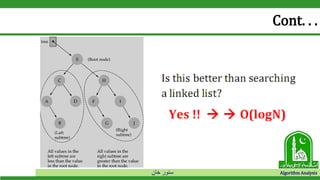
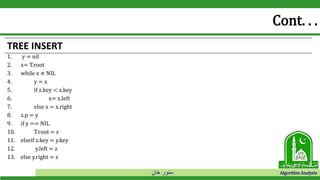
The document discusses binary search trees and their operations. It defines key concepts like nodes, leaves, root, and tree traversal methods. It then explains how to search, insert, find minimum/maximum elements, and traverse a binary search tree. Searching a BST involves recursively comparing the target key to node keys and traversing left or right. Insertion finds the appropriate position by moving pointers down the tree until reaching an empty node.
























![خان سنور Algorithm Analysis
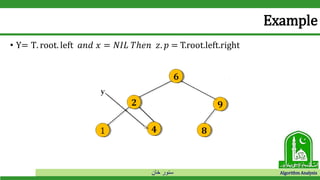
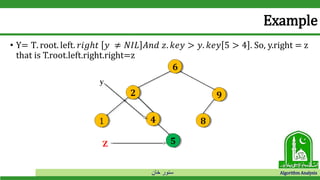
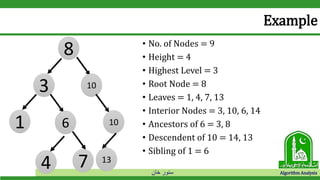
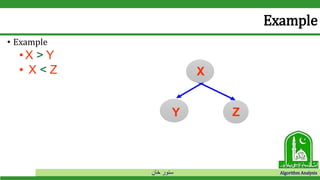
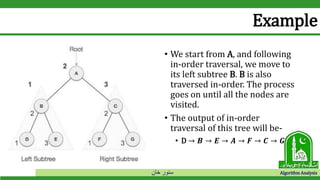
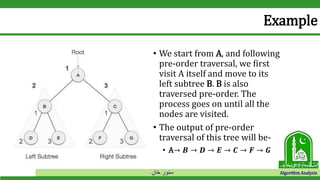
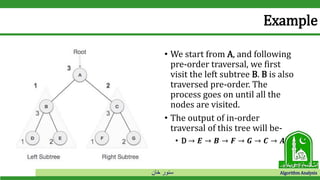
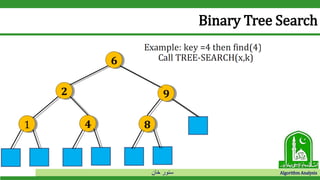
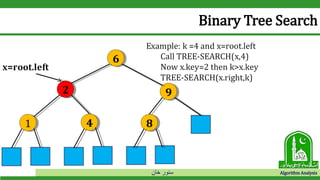
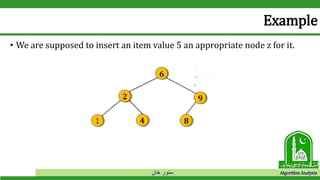
Example
• Now x ≠ 𝑁𝐼𝐿 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑧. 𝐾𝑒𝑦 < 𝑥. 𝑘𝑒𝑦 𝑇ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑖𝑠 [5 < 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-190528012407/85/Binary-Search-Tree-51-320.jpg)
![خان سنور Algorithm Analysis
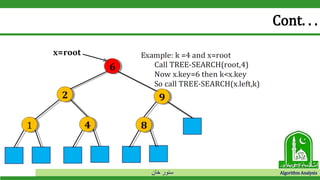
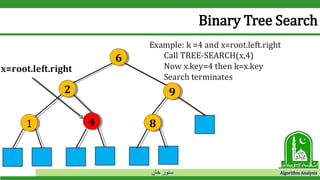
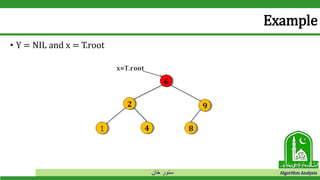
Example
• Now Y= T. rot 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 = 𝑇. 𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑡. 𝑙𝑒𝑓𝑡 𝐴𝑛𝑑 𝑧. 𝐾𝑒𝑦 > 𝑥. 𝑘𝑒𝑦 𝑇ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑖𝑠 [5 > 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-190528012407/85/Binary-Search-Tree-52-320.jpg)
![خان سنور Algorithm Analysis
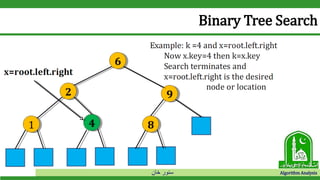
Example
• Y= T. root. left 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥 = 𝑇. 𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑡. 𝑟𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡 𝐴𝑛𝑑 𝑧. 𝐾𝑒𝑦 > 𝑥. 𝑘𝑒𝑦 𝑇ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑖𝑠 [5 > 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst-190528012407/85/Binary-Search-Tree-53-320.jpg)